Imagine a world without motors – no humming refrigerators, no whirring factory machines, no buzzing electric vehicles. It’s hard to fathom, isn’t it? These powerful devices, silently driving our world, rely on a complex network of electrical connections, and at the heart of this network lies the motor starter – a crucial component that controls the flow of power to the motor, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
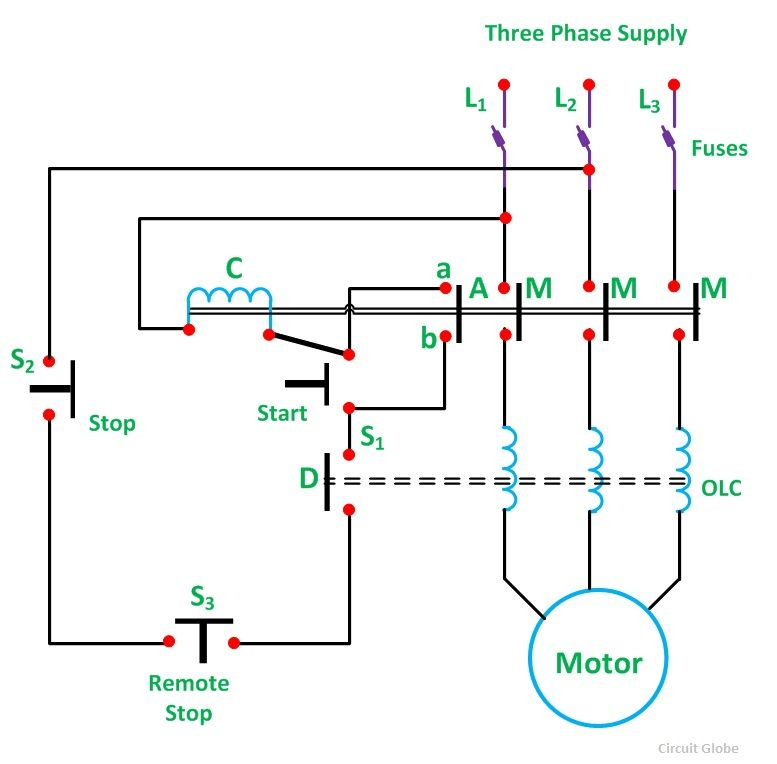
Image: wirelistobliquity.z19.web.core.windows.net
For anyone working with three-phase motors, understanding motor starter wiring diagrams is essential. This isn’t just about the technicalities; it’s about safety, efficiency, and ultimately, maximizing the lifespan of your equipment. In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of three-phase motor starter wiring diagrams, breaking down the components, the connections, and the reasons behind the design.
Understanding the Essentials: Components and Concepts
Before we dive into the intricacies of the diagrams, let’s first understand the key components and concepts behind them:
1. The Motor
The core of the system, a three-phase motor runs on alternating current (AC) power, utilizing three phases to generate a rotating magnetic field that drives the motor shaft. Each phase carries current at a specific voltage and phase angle, resulting in a constant, smooth rotation.
2. The Motor Starter
This is the control center for your motor. A motor starter is designed to protect the motor from overload, short circuits, and overcurrents. It also controls the starting and stopping of the motor. There are various types of motor starters, each with its specific features and applications:
- Magnetic Motor Starters: The most common type, these utilize an electromagnet to close the contacts, connecting power to the motor. They are reliable and offer several protection features.
- Solid-State Motor Starters: These use electronic components to control the motor, offering precise control, reduced wear and tear, and energy savings.
- Combination Motor Starters: This type often combines both magnetic and solid-state components, offering a hybrid solution with the advantages of both.
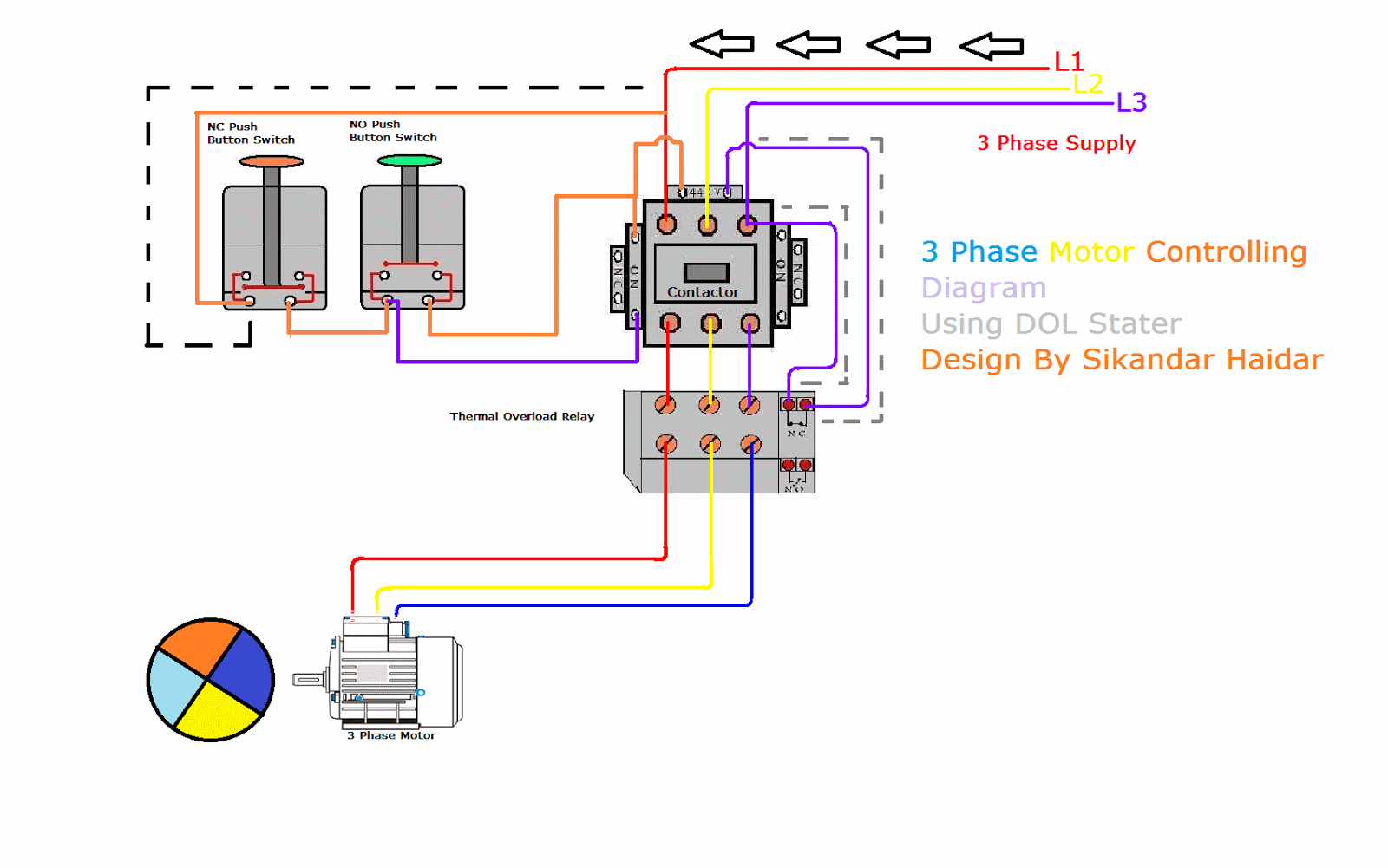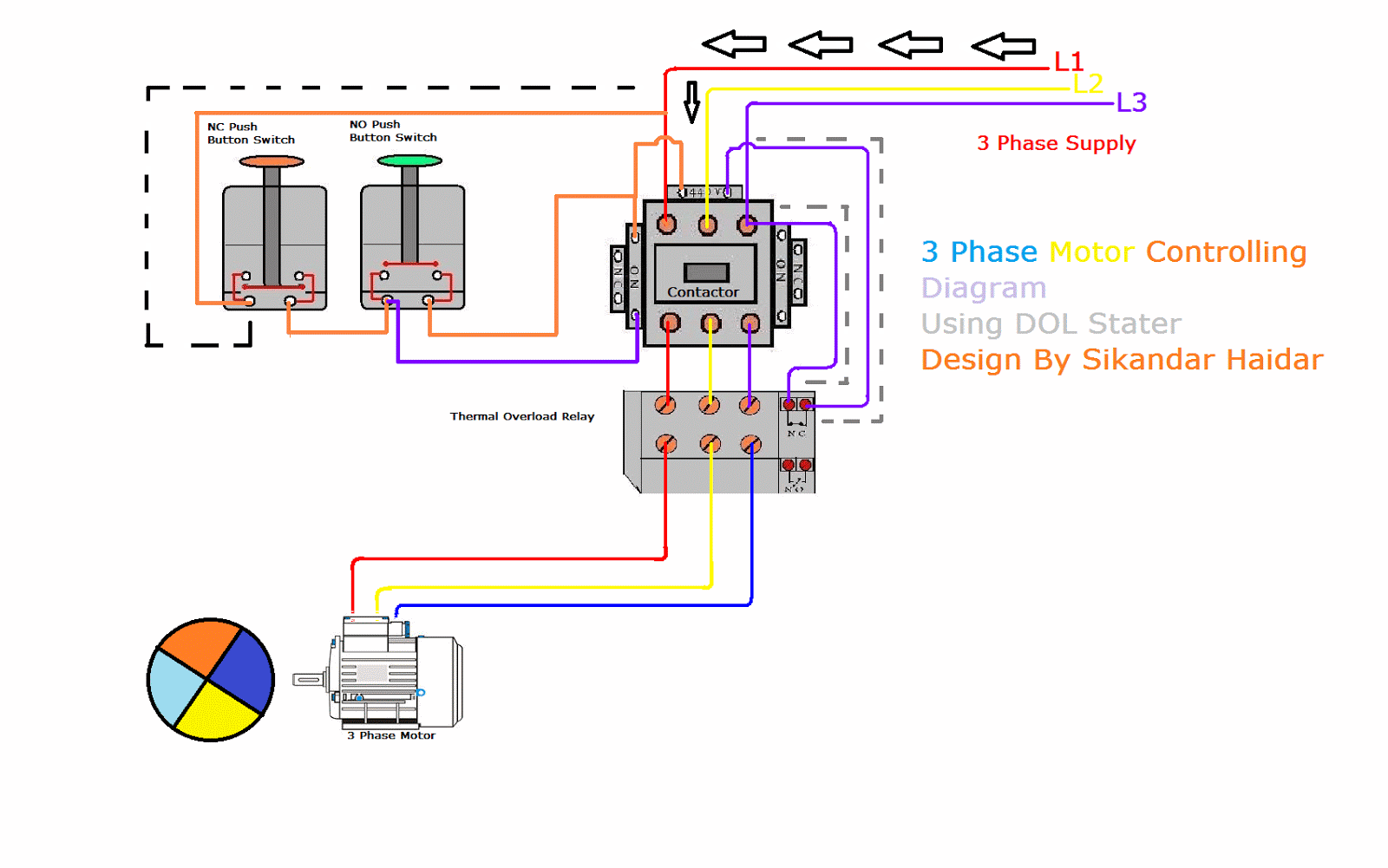
Image: fixpartlawrence.z1.web.core.windows.net
3. The Wiring Diagram
The heart of the system, the wiring diagram provides a visual representation of the electrical connections between the motor starter, the motor, and the power supply. By following this diagram, electricians can ensure correct and safe connections.
4. Three-Phase Power
Three-phase power is the standard for industrial and commercial applications. It consists of three separate AC voltage waveforms, each displaced by 120 degrees, creating a constantly rotating magnetic field. This provides a more consistent and efficient power supply compared to single-phase power.
Deciphering the Diagram: Key Elements and Connections
Now, let’s break down the essential components and connections within a typical three-phase motor starter wiring diagram:
1. Main Power Supply and Overload Protection: The Heart of the System
The diagram will show the main power supply, typically a three-phase line entering the starter. It will also depict the fuses or circuit breakers, which provide short-circuit protection. An overload relay is critical for motor protection, sensing excessive current and tripping the starter to prevent damage.
2. The Control Circuit: Commanding the Motor
This circuit is responsible for controlling the start and stop functions of the motor. It often involves push buttons or other control devices that send signals to the starter. The control circuit may also include auxiliary contacts that allow for additional functions, such as interlocking or signaling.
3. The Starter Coil and Motor Contacts: Relaying the Command
The starter coil is connected to the control circuit. When energized, it activates the electromagnet inside the starter, closing the motor contacts and allowing current to flow to the motor. The motor contacts are typically fused or protected against overload, protecting the motor from excess current.
4. Understanding Symbols and Notation
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent components. Familiarity with these symbols is critical for interpretation:
- L1, L2, L3: These symbols represent the three phases of the power supply.
- T1, T2, T3: These symbols represent the three terminals of the motor winding.
- S1, S2, S3: These symbols often represent the starter contacts.
- M: This symbol represents the motor.
- OL: This symbol represents the overload relay.
- F: This symbol represents fuses or circuit breakers.
Real-World Applications: Seeing the Wiring Diagram in Action
Let’s bring this concept to life with some real-world examples of how three-phase motor starter wiring diagrams are used in various industries:
1. Industrial Processes: Conveyor Belts and Production Lines
In factories, conveyor belts and production lines often rely on three-phase motors to drive machinery. The wiring diagram is crucial for ensuring the motor is properly connected and protected, ensuring efficient operation and preventing potential problems.
2. HVAC Systems: Keeping Buildings Comfortable
HVAC systems rely on powerful three-phase motors to drive fans, pumps, and compressors. The wiring diagram ensures proper connections and protection, ensuring the HVAC system operates effectively and safely, maintaining climate control in buildings.
3. Elevators: Moving People Up and Down
The electric motors in elevators require precise control and protection, and three-phase motor starter wiring diagrams ensure this. These diagrams guide the safe and reliable operation of elevators, ensuring passenger safety and smooth operation.
Safety First: Always Approach Wiring with Caution
Working with electrical systems, especially high-voltage three-phase power, demands the utmost caution. Always adhere to safety procedures and consult with qualified electricians if you’re unsure about any aspect of the wiring diagram:
- Never attempt any wiring work if you are not qualified and appropriately trained.
- Always disconnect the power source before working with electrical components.
- Verify the electrical system is properly grounded to minimize the risk of electric shock.
- Use appropriate safety equipment, including insulated tools and gloves.
- Consult the manufacturer’s instructions and specifications for the specific motor starter and motor you are working with.
New Trends and Developments: The Future of Motor Control
The field of motor control is constantly evolving, with new technologies and advancements emerging. These advancements are improving efficiency, safety, and control precision:
- Smart Motors and Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity: Motors are getting smarter, integrating sensors and connectivity to transmit data about performance and health, allowing for predictive maintenance and optimized operations.
- Variable-Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs offer precise speed control of AC motors, enabling applications requiring variable speed, such as pumps, fans, and conveyors.
- Energy Efficiency: New motor designs and control technologies aim to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental impact. Renewable energy sources are also playing a significant role in powering industrial motor systems.
Motor Starter Wiring Diagram 3 Phase
https://youtube.com/watch?v=o3-11_rzWGw
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Motor Control
Understanding three-phase motor starter wiring diagrams is essential for anyone involved in electrical work, particularly in industrial and commercial settings. By understanding the components, connections, and safety precautions, you can ensure the safe and efficient operation of your motor systems. As we continue to embrace new technologies, knowledge of motor control will remain a crucial skill, enabling you to harness the power of these essential machines for innovation and progress.
Remember, if you’re unsure about any aspect of electrical wiring, always consult a qualified electrician. By mastering the knowledge of motor control, you can contribute to safer, more efficient, and reliable operations in any industry where motors play a vital role.






