Picture this: you’re streaming your favorite show on your phone, but the internet connection is spotty, causing frustrating buffering. This is a common scenario in today’s interconnected world, where data demands are growing rapidly, and traditional cloud computing struggles to keep up with the need for low latency and high availability. Enter edge computing, a game-changer that brings processing power closer to the source of data, revolutionizing the way we deliver digital services.

Image: www.perlego.com
Kubernetes, the powerful open-source container orchestration platform, has emerged as a key player in edge computing. This combination unlocks a powerful synergy, enabling businesses to deploy and manage applications at the edge efficiently and effectively. This article will delve into the world of edge computing systems with Kubernetes, exploring its core principles, benefits, use cases, and the future of this exciting technology.
Understanding the Edge
The term “edge” in edge computing refers to the network’s periphery, where data is generated and consumed. Think of it as the “last mile” of data delivery, closer to users, devices, and sensors. Edge computing systems process data locally, reducing the need for constant communication with centralized data centers. This proximity significantly reduces latency and improves responsiveness, making edge computing ideal for real-time applications and critical data processing.
The Power of Kubernetes
Kubernetes is like the conductor of an orchestra, managing and orchestrating containers in a distributed environment. It provides a robust framework for:
- Container Deployment and Management: Kubernetes automates the process of deploying, scaling, and managing containers, ensuring smooth application operations.
- Service Discovery and Load Balancing: It connects applications seamlessly, ensuring high availability and optimal resource distribution.
- Network and Security Management: Kubernetes offers comprehensive network connectivity and security features, safeguarding applications and data.
- Self-Healing and Rollback: It automatically detects and recovers from failures, ensuring application resilience.
Edge Computing Systems with Kubernetes: A Winning Combination
When Kubernetes meets edge computing, a powerful synergy emerges, making it possible to:
- Deploy and Manage Applications at the Edge: Kubernetes provides a unified platform for deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications at the edge, simplifying operations.
- Enable Real-Time Data Processing: With edge processing, applications can respond to data in real-time, crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and IoT.
- Reduce Latency and Improve Responsiveness: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing eliminates the latency associated with cloud-based solutions.
- Ensure Scalability and Flexibility: Kubernetes’ architecture allows for seamless scaling of applications to meet ever-changing demands.
- Enhance Security: Kubernetes provides strong security features, protecting data and applications from vulnerabilities at the edge.
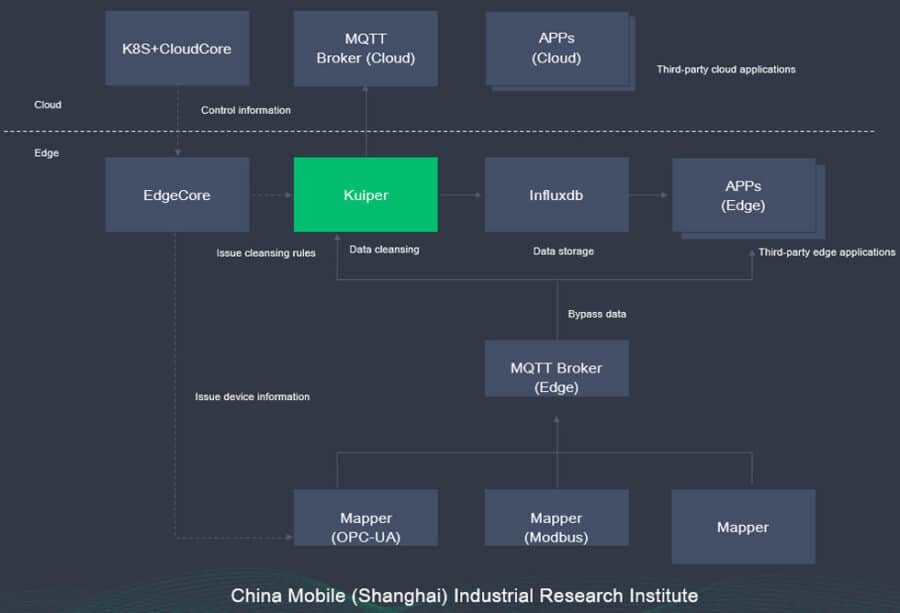
Image: www.cncf.io
Use Cases for Edge Computing Systems with Kubernetes
The applications of edge computing systems with Kubernetes are vast and diverse. Here are a few examples:
1. Industrial Automation
Industrial automation relies on real-time data analysis and control. Edge computing systems with Kubernetes can process data from sensors and equipment, enabling:
- Predictive Maintenance: Identifying potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and costs.
- Optimized Operations: Improving efficiency and productivity by analyzing real-time data and adjusting processes.
- Enhanced Safety: Detecting and mitigating safety hazards in real time.
2. Smart Cities
Smart cities are leveraging edge computing to enhance urban infrastructure and citizen services. Kubernetes enables:
- Traffic Management: Real-time analysis of traffic flow, optimizing traffic light synchronization and reducing congestion.
- Smart Lighting: Adjusting street lighting based on real-time conditions, optimizing energy consumption.
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring air quality, noise pollution, and other environmental parameters to improve public health.
3. Retail
The retail industry uses edge computing for:
- Personalized Experiences: Tailoring product recommendations based on real-time shopper behavior and preferences.
- Inventory Management: Tracking inventory levels in real time, optimizing stock and reducing waste.
- Queue Management: Optimizing checkout lines and wait times, improving customer satisfaction.
4. Healthcare
Edge computing is transforming healthcare by:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Enabling continuous health monitoring from home, providing faster intervention in emergencies.
- Telemedicine: Facilitate real-time consultations between patients and doctors, improving accessibility and reducing travel time.
- Medical Imaging Analysis: Processing medical images locally, reducing latency and enabling faster diagnoses.
Challenges and Considerations
While edge computing systems with Kubernetes offer significant benefits, it’s important to consider potential challenges:
1. Security
Data security is paramount in edge computing. With data spread across multiple locations, security threats become more complex. Kubernetes offers robust security features, but a comprehensive security strategy is essential. Implementing network segmentation, access control, and encryption is crucial for safeguarding data at the edge.
2. Management and Monitoring
Managing and monitoring edge deployments can be challenging, as infrastructure is distributed across multiple locations. Kubernetes provides tools for centralizing management, but adopting effective monitoring practices is essential. Implementing monitoring solutions that provide real-time insights and alerts is vital for ensuring smooth operations.
3. Network Connectivity
Reliable and high-bandwidth network connectivity is crucial for edge deployments. Network latency can impact application performance. Consider using a network architecture that caters to edge connectivity requirements, such as multi-cloud or hybrid cloud setups.
The Future of Edge Computing Systems with Kubernetes
The future of edge computing systems with Kubernetes is bright. Emerging technologies and trends are driving innovation:
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G and next-generation cellular networks will provide the bandwidth and latency needed for widespread edge adoption.
- AI and ML at the Edge: Edge computing is enabling AI and ML algorithms to operate closer to the data source, enabling real-time insights and decision-making.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless platforms are becoming increasingly popular in edge environments, simplifying development and deployment.
- Edge Cloud: New edge cloud platforms are emerging, offering dedicated infrastructure and services for edge applications.
Edge Computing Systems With Kubernetes Pdf
https://youtube.com/watch?v=bPtQOU9Blp4
Conclusion
Edge computing systems with Kubernetes offer a powerful solution for delivering digital services with low latency, high availability, and scalability. It’s a technology that empowers businesses to harness the power of data at the edge, enabling innovative applications across various industries. As we move towards a more interconnected and data-driven world, this powerful combination is poised to reshape the future of computing.






