Remember those frustrating physics classes, where the teacher drew diagrams of circuits with light bulbs and wires, and we were left to decipher the flow of electricity? The concept of circuits might have seemed daunting then, but understanding the basics of series and parallel circuits is foundational to comprehending how electricity works, whether for simple projects like building a light fixture or for complex systems like smartphones. This article will guide you through the essential concepts of series and parallel circuits, providing a comprehensive understanding of a series and parallel circuits worksheet answer key.
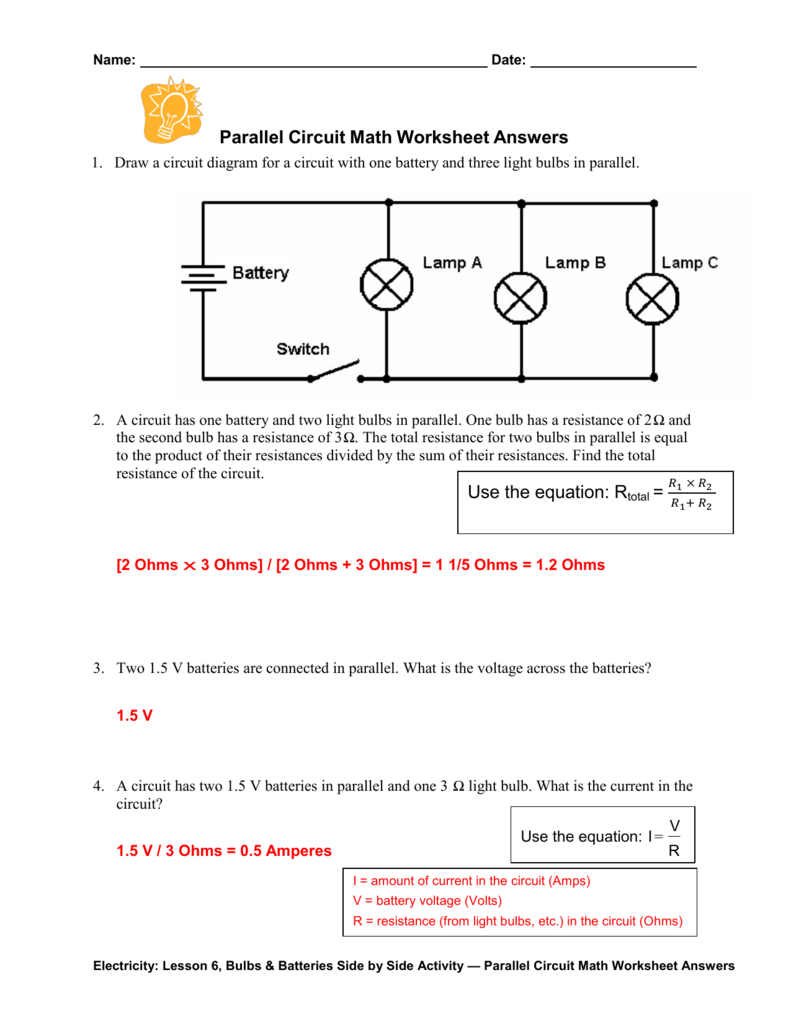
Image: lessonfullfrancie.z21.web.core.windows.net
Imagine a time when you were trying to build a simple light circuit. You had the wires, the bulb, and the battery, but couldn’t figure out how to connect them. Then, you discovered series and parallel circuits and their functionalities on a worksheet. That’s when the magic of electricity clicked! Understanding those fundamental concepts not only helped you complete your project but also ignited your curiosity about the fascinating world of electrical circuits.
Understanding Series and Parallel Circuits
Series and parallel circuits are two fundamental ways to arrange electrical components. Understanding their differences and similarities is crucial for effectively using and troubleshooting electrical systems. A series circuit, as its name suggests, involves components connected one after the other in a single path. The current flows through each component sequentially, making it a single pathway for electricity. Conversely, in a parallel circuit, multiple paths are available for the current to flow, with components connected alongside each other. This means the current can flow through different components simultaneously.
The Fundamentals of Series and Parallel Circuits
Series Circuits
In a simple series circuit, the current goes through each component in order, like a single line of people walking through a doorway. For example, imagine a Christmas light string with 10 lights; all those lights are connected in a series circuit. If one bulb burns out, the circuit breaks, and all the lights go out. This is because the current has no alternative route to flow through. This is why older Christmas lights often had one broken bulb, and the entire string would go dark.

Image: manualmanualleona.z6.web.core.windows.net
Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, the current splits into multiple pathways, like a fork in a road where traffic diverges. Imagine a house’s electrical system, where each room is wired separately on the same circuit. The result? Turning on a light in one room won’t affect the other rooms’ lights. If one light bulb burns out, the others will continue to shine—why? Because the current has an alternate route to flow through, ensuring continuity. This is why home circuits are generally designed with parallel configurations.
Key Differences
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between series and parallel circuits:
| Feature | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Current Flow | Single path | Multiple paths |
| Resistance | Total resistance is the sum of individual resistances | Total resistance is the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances |
| Voltage | Voltage is divided among components | Voltage is the same across all components |
| Effect of a component failure | Circuit breaks, all components stop working | Other components continue working |
The Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheet Answer Key
A series and parallel circuits worksheet is a valuable tool for learning and testing your understanding of these circuit types. The worksheet typically contains diagrams of circuits with different configurations and asks questions about current, voltage, and resistance. To successfully answer these questions, you need a firm understanding of the following concepts:
Ohm’s Law: V = IR (Voltage = Current x Resistance). This fundamental law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. Using Ohm’s law, you can calculate voltage, current, or resistance if you know the values of the other two.
Voltage: The potential energy difference between two points in a circuit that causes electrons to flow. In a series circuit, the voltage is divided among the components, while in a parallel circuit, it remains the same across all components.
Current: The rate of flow of electrical charge through a circuit. In a series circuit, the current is the same for all components, while in a parallel circuit, it splits across the different paths.
Resistance: The opposition to the flow of current in a circuit. Components like resistors, wires, and even light bulbs offer resistance to the current’s flow. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, it is calculated as the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances.
Tips and Expert Advice for Mastering Series and Parallel Circuits
Tackling a series and parallel circuits worksheet can be challenging, but certain techniques can greatly simplify the process and enhance your understanding.
First, draw clear diagrams of the circuit, labeling all components and including their values. This visual representation will make it easier to visualize the flow of current and identify any potential issues. Second, use color-coding to visually distinguish between different components, current paths, and voltage drops. This technique will help you stay organized and avoid confusion. Finally, start with simple circuits and gradually increase the complexity. This gradual approach will allow you to build a strong foundation before tackling more complex problems.
Practice diligently by attempting different problems and comparing your answers to the answer key. This will help you identify areas where you need further clarification. Additionally, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher or a tutor for help. They can provide personalized guidance and address specific questions you might have.
FAQs about Series and Parallel Circuits
Here are some frequently asked questions about series and parallel circuits:
Q: What is the difference between a short circuit and a parallel circuit?
A: A short circuit is a dangerous situation where the current follows an unintended path with very low resistance, potentially leading to excessive heat and damage. By contrast, a parallel circuit is a safe design where current splits into multiple paths, offering alternatives to flow and reducing potential hazards.
Q: Can a series circuit be used for household wiring?
A: No, series circuits are not suitable for household wiring due to their inherent disadvantage of breaking the entire circuit if one component fails. House wiring utilizes parallel circuits to ensure that if a light bulb burns out, other lights remain functional.
Q: Is it possible to have a combination of series and parallel circuits?
A: Yes, many real-world circuits are a combination of series and parallel elements. For example, a circuit powering two lamps in your house might have parallel connections for each lamp but be connected to the main power supply in series.
Series And Parallel Circuits Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamentals of series and parallel circuits is crucial for navigating the world of electronics and electrical systems. Whether you’re building a simple project or working with complex electrical grids, proficiency in these concepts is essential. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of series and parallel circuits and how to effectively use a series and parallel circuits worksheet answer key. Are you ready to tackle your next electrical challenge?






