Imagine peering into the heart of a single element, say carbon. You might picture identical, tiny spheres. You wouldn’t be wrong, but the truth is a bit more nuanced – a fascinating dance of subtle differences that define the world around us. While all atoms of a given element share the same number of protons, their identity extends beyond that. Enter the realm of isotopes, revealing the intricate variations that give elements their unique properties and fuel countless applications.
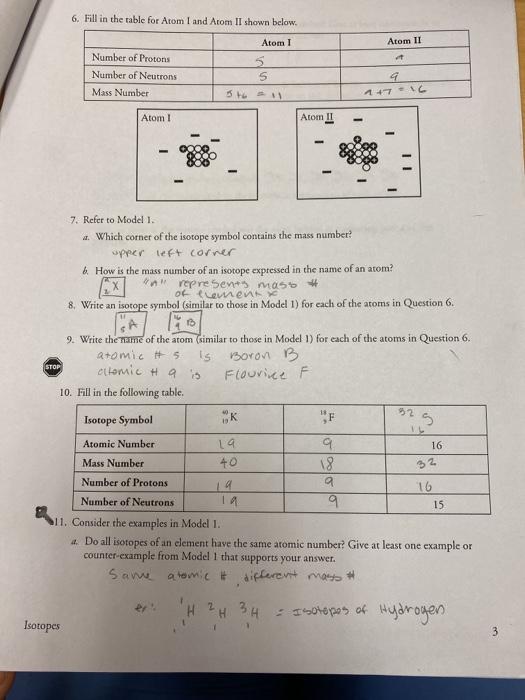
Image: www.chegg.com
Understanding isotopes is crucial for grasping the essence of chemistry and physics. They explain the existence of radioactive elements, the workings of nuclear reactors, and even the origins of the universe itself. This article delves into the fascinating world of isotopes, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and profound impact on our lives.
The Atom’s Unseen Complexity: Introducing Isotopes
The fundamental building blocks of matter, atoms, are characterized by their protons, neutrons, and electrons. The number of protons, known as the atomic number, defines an element’s identity. Carbon, with six protons, will forever be carbon, regardless of its other constituents. But the number of neutrons can vary, creating isotopes – atoms of the same element with different masses.
Imagine a family portrait. Each member shares a common lineage, a common identity (in this analogy, the atomic number), yet each individual carries their own unique features (the number of neutrons). Carbon-12, the most common form of carbon, has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Its sibling, Carbon-14, boasts the same six protons but adds two extra neutrons, giving it a greater mass. They both remain carbon, but their differences have profound implications.
Beyond the Same Element: Exploring Isotopes’ Unique Traits
While isotopes are chemically similar, their differing neutron counts lead to distinct characteristics. This variation influences their stability, radioactivity, and even their role in biological processes. Understanding these differences is key to unraveling the secrets of the universe and harnessing the power of isotopes in diverse applications.
Stability, Radioactivity, and the Dance of Decay
Some isotopes, like Carbon-12, are stable, meaning they exist indefinitely without decaying. Others, such as Carbon-14, are radioactive. Their excess neutrons make them unstable, leading to the emission of particles and energy as they transform into stable forms. This release of energy, often in the form of radiation, is at the heart of nuclear processes.
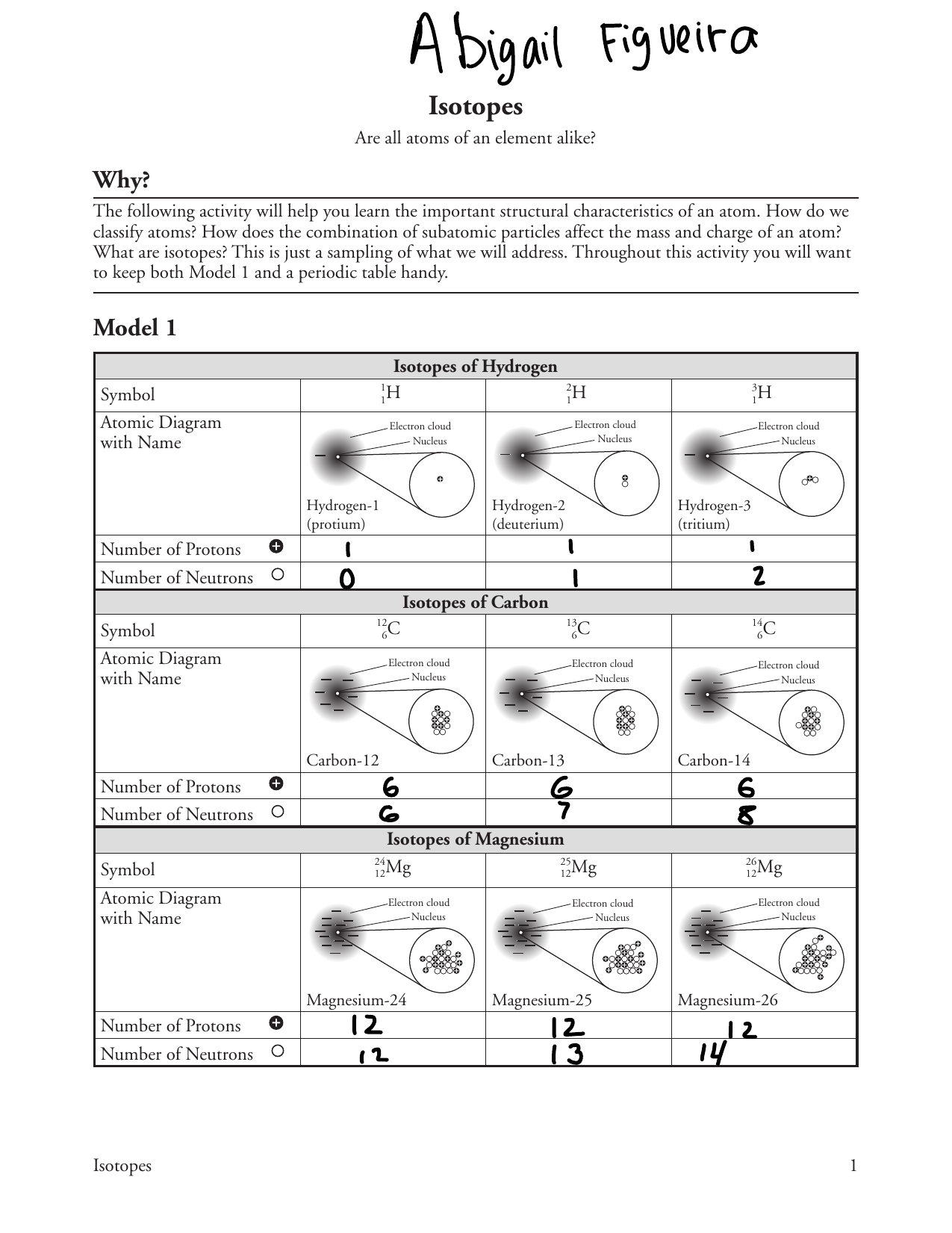
Image: studylib.net
Isotopes and the Spectrum of Applications
The world of isotopes is vast, extending far beyond textbooks and lab experiments. Their unique properties find applications in numerous fields, from understanding the past to advancing medicine.
A Window to the Past: Isotopes in Dating and Archaeology
Radioactive isotopes serve as timekeepers, allowing us to unravel the mysteries of the past. Carbon-14 dating, for instance, leverages the radioactive decay of Carbon-14 to determine the age of ancient artifacts, fossils, and even Earth itself. The known half-life of Carbon-14, the time it takes for half of the isotope to decay, provides a precise clock to measure the passage of millennia.
Other radioisotopes like Uranium-238 also play a key role in geological dating, giving us insights into the Earth’s formation and evolution. The decay of these isotopes provides a unique fingerprint, allowing scientists to reconstruct the Earth’s history and understand the processes shaping our planet.
Harnessing the Power: Isotopes in Medicine and Industry
The power of isotopes extends beyond uncovering the past, driving innovation in medicine and industry. Radioactive isotopes are used in medical diagnosis and treatment. They enable sophisticated imaging techniques like PET scans, allowing doctors to visualize organs and pinpoint abnormalities. Specific isotopes like iodine-131 are employed in radiation therapy, targeting cancerous cells and minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Beyond medicine, isotopes are employed in various industrial processes. They are integral to manufacturing, quality control, and even environmental monitoring. For example, isotopes in tracers are used to track the flow of materials in complex systems, improving production efficiency and reducing waste.
The Unseen Wonders: Isotopes and the Universe
Isotopes are not only shaping our present but are also revealing the secrets of the universe. The Big Bang theory, our best explanation for the universe’s birth, predicts the abundance of certain isotopes. The presence of these isotopes, observed throughout space, provides strong evidence for the Big Bang, offering insights into the universe’s origin and evolution.
Understanding isotopes is crucial for unveiling the universe’s secrets. Scientists meticulously analyze the compositions and ratios of isotopes in meteorites, comets, and even distant stars. These analyses unveil the history of our solar system, the processes driving stellar evolution, and even the potential for life on other planets.
Isotopes Are All Atoms Of An Element Alike
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Intricate World of Isotopes
The world of isotopes is a testament to the intricacies and beauty of the natural world. They reveal that even atoms, the supposed building blocks of matter, harbor unexpected variations. These variations are not mere curiosities; they fuel scientific discoveries, drive technological advancements, and provide clues to the origins of our universe. So, next time you think of an element, remember that beneath the surface lies a fascinating array of isotopes, each with its own story to tell.
This journey into the world of isotopes is just the beginning. The possibilities are vast, and there is still much to discover. We encourage you to explore further, delve into specific applications, and appreciate the remarkable impact of isotopes on our lives and our understanding of the universe.






