Have you ever found yourself struggling to retain information from a lecture or textbook, only to realize you’re relying entirely on external resources to understand the material? This can be a common experience, especially in the fast-paced environment of modern education. But what if there was a way to learn more effectively, without the need for constant external support? The key lies in developing independence as a learner.
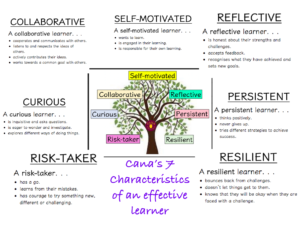
Image: www.canahillside.catholic.edu.au
Independent learners are individuals who possess the crucial skills and mindset to take ownership of their education. They actively pursue knowledge, dissect information, and develop a deep understanding of concepts, all without relying heavily on others. Their journey is marked by self-directed exploration, critical thinking, and a relentless thirst for knowledge. By understanding the key characteristics of an independent learner, you can embark on your own journey towards becoming a more effective and empowered student.
1. Self-Motivation and Ownership
The Engine of Learning
At the heart of an independent learner lies unwavering self-motivation. Instead of waiting for external deadlines or pressure to propel them forward, these individuals are driven by an intrinsic desire to learn and a genuine curiosity about the world around them. This inner drive leads them to actively seek out new knowledge and challenges, even beyond the confines of a classroom or curriculum. They see learning as an enriching experience, not a chore.
Taking the Reins
This intrinsic motivation translates to a sense of ownership over their educational journey. They don’t simply passively consume information; they engage with it actively, asking questions, making connections, and applying what they learn to real-world scenarios. By taking responsibility for their learning, they become masters of their own intellectual growth.

Image: www.slideshare.net
Examples:
Imagine a student who, after learning about a specific historical event, decides to delve deeper into the social and political context of that time period by reading primary sources and exploring historical documentaries. This doesn’t happen because a teacher assigns it; this arises from the student’s self-motivation and desire to understand the broader implications of what they’ve learned.
2. Goal Setting and Planning
Charting the Course
Independent learners are masters of their own learning trajectories. They have a clear vision of what they want to achieve, setting specific goals and outlining a roadmap to reach them. This might involve identifying knowledge gaps, setting learning objectives, and choosing resources that align with their learning styles and aspirations.
Staying on Track
Effective planning is key. Independent learners understand the power of breaking down large goals into smaller, manageable steps. This allows them to track their progress, celebrate milestones, and adapt their plans if necessary. They are not afraid to re-evaluate their approach and adjust their course based on their own experiences and insights.
Examples:
A student aiming to acquire fluency in a new language might set a goal of learning 10 new vocabulary words each day, creating a schedule for practicing pronunciation, and booking online sessions with a native speaker to enhance their conversational skills. This structured approach helps them stay on track and achieve their overall language acquisition goals.
3. Effective Time Management
Mastering the Art of Balance
Life is full of competing demands, and independent learners have mastered the art of balancing their commitments. They understand the importance of prioritizing tasks, allocating time effectively, and developing strategies to avoid procrastination. They are disciplined in their time management habits, ensuring they dedicate sufficient time to learning without sacrificing other important aspects of their lives.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Effective time management also involves flexibility. Independent learners are adept at adjusting their schedule based on unforeseen circumstances, whether it’s a sudden influx of work commitments or an unexpected opportunity to engage with a particularly stimulating topic. They don’t get rigid with their plans but rather adapt to the ebb and flow of their lives, ensuring learning remains a priority.
Examples:
Think of a student juggling a part-time job, extracurricular activities, and a demanding academic schedule. By strategically planning their time, effectively prioritizing tasks, and managing their workload, they can carve out dedicated time for learning, ensuring they keep up with their studies without burnout.
4. Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Questioning and Analyzing
Independent learners are not passive absorbers of information; they actively question what they learn and analyze information from multiple perspectives. They are constantly seeking to understand the “why” behind the “what.” This critical approach helps them identify inconsistencies, evaluate the credibility of sources, and develop well-rounded perspectives.
Finding Solutions
Critical thinking is inherently tied to problem-solving. Independent learners relish challenges and approach them with a methodical mindset. They break down complex issues into smaller parts, explore alternative solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness. They are not afraid to experiment, learn from their mistakes, and refine their problem-solving strategies over time.
Examples:
Consider a student tasked with writing an essay on a controversial topic. Instead of simply regurgitating facts from textbooks, they critically examine different viewpoints, identify the strengths and weaknesses of each argument, and formulate their own well-reasoned conclusion based on their analysis.
5. Active Information Seeking
Beyond Traditional Sources
Independent learners are not confined to textbooks and lectures. They seek knowledge from diverse sources, including online articles, podcasts, documentaries, research papers, and even interviews with experts. They understand that learning goes beyond the confines of a classroom and embrace the opportunity to engage with various perspectives and formats to expand their understanding.
Curated Learning Experiences
This active search for information also involves curation. They identify reliable sources, filter out irrelevant information, and prioritize content that aligns with their learning goals. This discerning approach allows them to build a comprehensive understanding of a topic, drawing insights from multiple perspectives and avoiding the pitfalls of misinformation.
Examples:
A student interested in environmental sustainability might delve into research papers about climate change, listen to podcasts discussing sustainable practices, watch documentaries highlighting environmental challenges, and even participate in local environmental initiatives to gather firsthand insights.
6. Effective Note-Taking and Organization
Capturing the Essence
Independent learners recognize the importance of effective note-taking as a way to organize, process, and retain information. They develop their own unique style, whether it involves mind mapping, bullet points, or detailed summaries. The key is to capture the essence of what they learn in a way that is meaningful and easily accessible for future review.
Building a Knowledge Base
Organization is equally important. Independent learners structure their notes in a way that facilitates understanding and retrieval. They create folders, use digital tools, or employ physical systems to maintain a well-organized collection of their learning materials. This allows them to revisit key concepts, make connections between different topics, and build a comprehensive knowledge base over time.
Examples:
A student studying a complex subject like physics might create digital flashcards for key formulas, organize their notes into chronological order, and use mind maps to connect different concepts. This structured approach helps them effectively manage a large volume of information and readily access it when needed.
7. Effective Communication and Collaboration
Sharing and Discussing
Independent learners recognize that learning is not a solitary endeavor. They actively engage in discussions, share their insights, and collaborate with peers to gain fresh perspectives and deepen their understanding. This might involve participating in online forums, joining study groups, or even initiating conversations with experts in their field of interest.
Building a Network of Support
Communication also encompasses seeking help when needed. Independent learners are not afraid to ask for clarification or guidance from teachers, mentors, or peers. They understand that collaboration can be a powerful tool for learning, and they are willing to embrace the support of others when necessary.
Examples:
A student working on a research project might reach out to a professor for guidance, join a study group to discuss research methodologies with peers, or engage in online forums to exchange ideas and learn from others working in the same field.
8. Adaptability and Resilience
Embracing Change
The world is constantly evolving, and independent learners recognize the need to adapt to change. They are open to new ideas, willing to experiment with different approaches, and comfortable adjusting their learning strategies based on their individual needs and the demands of their chosen field. They understand that learning is an ongoing journey, not a destination.
Overcoming Challenges
This adaptability also extends to their ability to bounce back from challenges. Independent learners are not discouraged by setbacks but rather view them as opportunities to learn, grow, and refine their approaches. They are resilient in the face of adversity, persevering through difficulties and emerging stronger with each new experience.
Examples:
Imagine a student struggling to grasp a complex mathematical concept. Instead of giving up, they seek tutoring support, explore online resources, and experiment with different teaching methods until they find an approach that resonates with their learning style. This determination and resilience are key characteristics of independent learners who embrace challenges as stepping stones to greater understanding.
9. Self-Reflection and Assessment
The Mirror of Learning
Independent learners are not afraid to look inward and assess their own progress. They engage in self-reflection, evaluating their strengths and weaknesses, identifying areas for improvement, and adjusting their learning strategies accordingly. They take ownership of their learning by being honest with themselves about their progress and constantly seeking ways to enhance their abilities.
Benchmarking Success
Self-assessment also involves setting benchmarks and tracking their performance against these objectives. Independent learners regularly evaluate their understanding of concepts, identify their learning gaps, and adjust their learning plans to ensure they are making meaningful progress towards their goals. They actively seek feedback from others to gain a holistic perspective on their performance.
Examples:
A student preparing for an exam might take practice tests to assess their understanding, analyze their strengths and weaknesses, and allocate more time to studying areas where they need extra practice. This self-reflection and assessment ensure they are effectively preparing for the exam and maximizing their chances of success.
10. Lifelong Learning Mindset
Independent learners don’t see learning as a finite process; they embrace it as a lifelong journey. They understand that education is not confined to formal settings and actively seek out opportunities to learn and grow throughout their lives. Their thirst for knowledge is insatiable, and they actively engage with the world around them, constantly expanding their horizons and refining their understanding.
Embrace the Unknown
This lifelong learning mindset involves a willingness to step outside of their comfort zones and embrace new experiences. They are not afraid of the unknown but rather view it as an opportunity to learn, grow, and contribute to the world around them. Their curiosity knows no bounds, and they are always eager to embark on the next chapter of their learning journey.
Examples:
Consider an individual who, after graduating from university, continues to enroll in online courses, attends workshops, reads industry publications, and engages in discussions with colleagues in their field. This lifelong pursuit of knowledge ensures they remain relevant, adaptable, and intellectually engaged throughout their lives.
10 Characteristics Of An Independent Learner
https://youtube.com/watch?v=shFL3Wr536k
Conclusion
Becoming an independent learner is not a destination but a journey. It is a continuous process of self-discovery, exploration, and growth. By cultivating these ten characteristics, you can empower yourself to take control of your education, become a more effective learner, and unlock your full potential. Remember, the pursuit of knowledge is a lifelong endeavor, and the rewards of becoming an independent learner are truly boundless.






