Remember that awkward moment in English class when you were asked to identify the parts of speech? You knew adjectives described nouns, but what about adverbs? Were they friends or foes? It’s easy to get confused, and frankly, those grammatical rules can seem like a foreign language. But fear not! This comprehensive guide dives into the world of adverbs, adjectives, nouns, and verbs, providing a clear understanding of their roles and functions.

Image: www.pinterest.com.au
We’ll explore their history, their purpose, and how they work together to create meaningful sentences. Think of this as a grammar cheat sheet, offering examples and insights to help you master these essential elements of the English language. So, let’s embark on this linguistic journey together and conquer those grammar demons once and for all.
Dissecting the Building Blocks of Language
These four parts of speech make up the core of any language, forming the foundation on which we build sentences and convey meaning. Let’s break them down one by one.
Nouns: Naming the World
Nouns are the foundation of any sentence. They represent people, places, things, and ideas. Think of them as the who and what of our language. Here are some examples:
- People: Student, doctor, artist, friend
- Places: School, hospital, museum, city
- Things: Book, phone, car, table
- Ideas: Happiness, love, courage, freedom
Verbs: Actions in Motion
Verbs are the action words of the language. They describe what someone or something is doing. Here’s how we identify them:
- Action Verbs: Run, jump, sing, write, eat
- State of Being Verbs: Be, seem, appear, feel, become
Verbs bring our sentences to life, painting vivid pictures of actions and states of being.
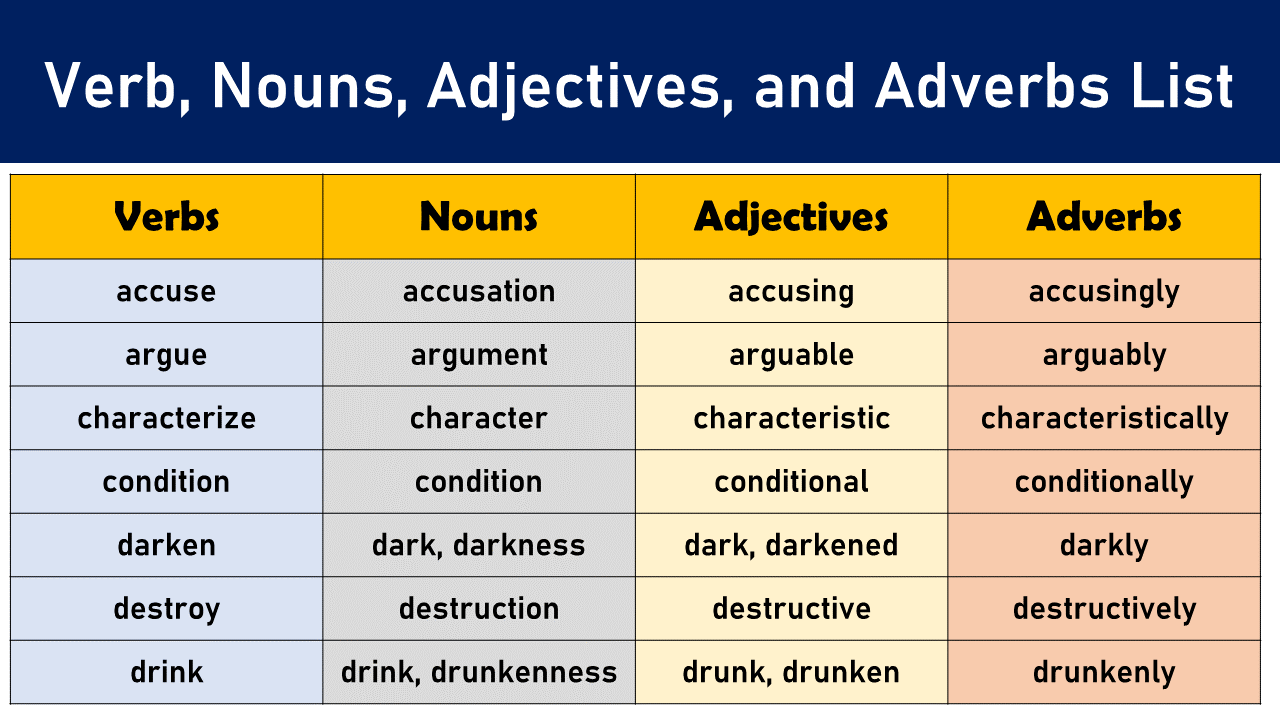
Image: engdic.org
Adjectives: Describing the World
Adjectives modify nouns, adding details and color to our descriptions. They tell us more about the noun, its qualities, and how it stands out. Examples include:
- Size: Big, small, tiny, enormous
- Color: Red, blue, green, yellow
- Shape: Round, square, flat, oval
- Quality: Happy, sad, funny, interesting
Adverbs: Modifying the Actions and Descriptions
Adverbs are the powerhouses of our sentences. They modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, adding shades of meaning, time, place, and manner.
- Time: Now, then, yesterday, tomorrow
- Place: Here, there, everywhere, nowhere
- Manner: Quickly, slowly, happily, sadly
- Degree: Very, extremely, quite, somewhat
Latest Trends in Language Use
The way we use language is constantly evolving, reflecting changes in our society and technology. Here are some interesting trends in the world of adverbs, adjectives, nouns, and verbs:
- Informal Language: The rise of social media has led to a more casual approach to language, with abbreviations, emojis, and slang expressions becoming more common.
- Inclusive Language: The focus on inclusivity has prompted changes in the way we use language, embracing more gender-neutral terms and avoiding stereotypes.
- Emerging Words: New words are constantly being coined to describe new technologies, ideas, and phenomena. This reflects our dynamic world.
Expert Tips and Advice
Here are some valuable tips to help you excel in your use of adverbs, adjectives, nouns, and verbs.
- Read Widely: Dive into books, magazines, and online articles. Pay attention to how authors use these parts of speech to create their narratives.
- Use a Thesaurus: Expand your vocabulary by exploring different synonyms for words. A thesaurus can be a valuable tool to avoid repetition and add variety to your writing.
- Practice! The more you write, the more comfortable you’ll become with using these parts of speech effectively.
Remember, understanding the grammar rules is just the beginning. The art of using language comes with practice and a passion for exploring the intricacies of the English language.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between an adjective and an adverb?
The key difference is that adjectives modify nouns while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. For example, “The *red* car is *very* fast.” Here, “red” modifies the noun “car” and “very” modifies the adjective “fast”.
Q: How do I know if a word is a noun, verb, adjective, or adverb?
The best way is to understand the word’s function in the sentence. Ask yourself, “What is this word doing?” If it names something, it’s a noun. If it describes an action, it’s a verb. If it describes a noun, it’s an adjective. And if it modifies another word, it’s an adverb.
Q: Can a word be more than one part of speech?
Absolutely! Many words can function as multiple parts of speech depending on their context in a sentence. Take the word “run” as an example:
- **Verb:** The dog *runs* in the park.
- **Noun:** We had a great *run* this morning.
List Of Adverbs Adjectives Nouns And Verbs
Conclusion
Understanding adverbs, adjectives, nouns, and verbs is crucial to mastering the English language. By familiarizing ourselves with their functions and exploring their nuances, we can write with clarity, precision, and creativity. Don’t be daunted by the rules of grammar—embrace them and see how they empower you to communicate effectively.
Are you ready to explore the world of language with confidence? Let us know in the comments below if you have any questions or share your tips for mastering these essential parts of speech!






