As a kid, I always found science experiments fascinating, particularly those involving plants. I remember growing sunflowers in my backyard, eagerly watching them sprout and grow taller each day. I couldn’t help but wonder what magical process was happening inside their green leaves, allowing them to transform sunlight into energy. My curiosity led me to learn about photosynthesis, the remarkable process plants use to sustain life. It wasn’t until I encountered the Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab that I truly grasped the intricate mechanisms of this vital process.
 Image: qwivy.com
Image: qwivy.comThe Gizmo lab, a virtual tool designed for interactive learning, offers students like myself a unique opportunity to discover the world of photosynthesis by simulating real-world experiments. This engaging platform allows us to manipulate variables, observe changes in plant growth, and ultimately acquire a deeper understanding of how plants function. So, whether you’re a student seeking help with your lab assignment or an individual curious about plant life, this article will guide you through the Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab, providing insights and answers to help you unlock the secrets of this essential process.
Understanding Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the process that sustains life on Earth, is a complex series of biochemical reactions that transform light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose. This chemical energy is then used by plants for growth, reproduction, and other vital functions.
The process occurs in specialized structures within plant cells called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs light energy. Think of chlorophyll as the solar panels of the plant world; they capture light energy and convert it into a usable form.
Photosynthesis can be summarized in two main stages:
- The Light-Dependent Reactions: These reactions occur in the chloroplast’s thylakoid membranes and require sunlight. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, triggering a chain of events that splits water molecules, releases oxygen, and produces ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells.
- The Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast, the region surrounding the thylakoids. ATP and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), another energy carrier molecule, are utilized along with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to synthesize glucose.
This process, also known as carbon fixation, is the foundation for life on Earth, as it provides the food source for all living organisms, directly or indirectly.
Navigating the Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab
The Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab provides a virtual environment that allows students to explore different aspects of photosynthesis in a safe and interactive manner. It offers various components, including:
- Light Source: Allows students to adjust the intensity of light to observe its effects on the rate of photosynthesis.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: Provides students the ability to modify the levels of carbon dioxide in the environment, simulating different atmospheric conditions.
- Temperature: Offers a platform for students to examine the impact of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis.
- Plant Species: The Gizmo provides data on the photosynthesis rates of different plant species, allowing for comparative analysis.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Students can record and analyze data, such as the rate of oxygen production, to understand the key factors influencing photosynthesis.
The interactive nature of the Gizmo allows students to perform virtual experiments, adjust variables, and analyze data, all in a simulated environment. This hands-on approach enhances learning and understanding of the intricate workings of photosynthesis.
Unlocking the Secrets of Photosynthesis: Tips and Tricks
Here are some tips to help you navigate the Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab and gain a deeper understanding of photosynthesis:
- Start with the basics: Begin with the default settings of the Gizmo and familiarize yourself with the components and basic functions.
- Experiment with variables: Modify individual variables, such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, or temperature, and observe their effects on the rate of photosynthesis. Record your observations and analyze the data to draw conclusions.
- Compare different plant species: Explore how different plant species respond to changes in environmental factors, comparing their photosynthesis rates.
- Use the graphing tools: Utilize the Gizmo’s graphing tools to visualize and analyze the relationship between the variables and the rate of photosynthesis. This will provide a clearer understanding of the trends and relationships.
- Reference outside resources: Refer to your textbook, scientific articles, or online resources to deepen your understanding of photosynthesis and how it relates to the Gizmo’s simulations.
By following these tips, you can unlock the secrets of photosynthesis, gain valuable insights into plant life, and improve your understanding of this essential biological process. Remember, the key to success is hands-on exploration and applying your knowledge to interpret the results you obtain.
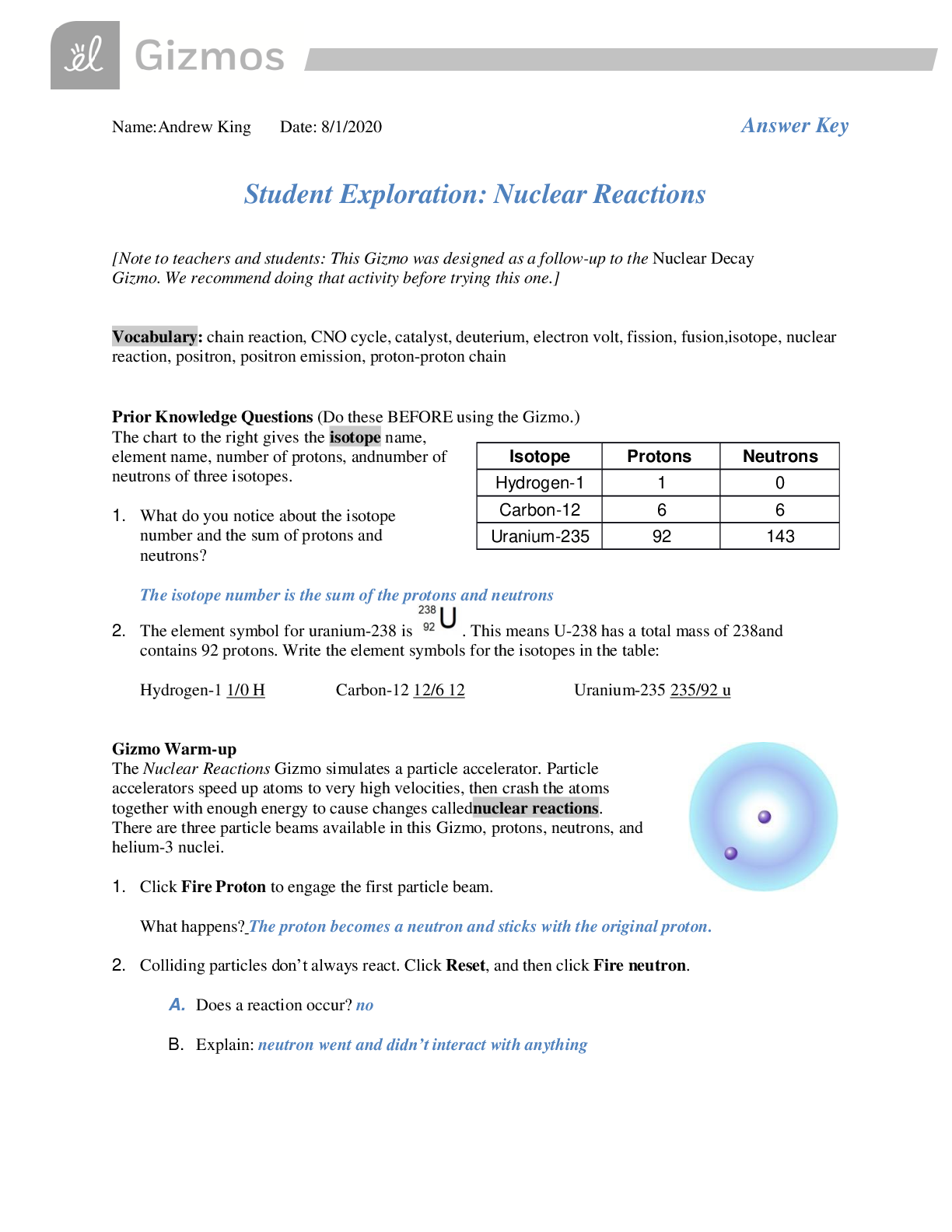
Image: browsegrades.net
FAQs about Photosynthesis and the Gizmo Lab
Q: What are the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
A: The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by several factors, including:
- Light intensity: The higher the light intensity, the greater the rate of photosynthesis, up to a certain point. This is because more light energy is available for the light-dependent reactions.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Increased carbon dioxide concentration generally leads to a higher rate of photosynthesis, as it provides more substrate for the Calvin cycle.
- Temperature: Photosynthesis has an optimal temperature range. Too low, and enzymatic reactions slow down; too high, and proteins can denature, hindering the process.
- Water availability: Plants need water for photosynthesis; a shortage can significantly decrease the rate of the process.
- Mineral nutrients: Essential minerals, like magnesium, are required for chlorophyll production and other important enzymatic reactions.
Q: What is the significance of photosynthesis?
A: Photosynthesis is the cornerstone of life on Earth. It provides the following:
- Food source: Plants, through photosynthesis, produce glucose, which is the source of energy for all living organisms, directly or indirectly.
- Oxygen production: Photosynthesis releases oxygen as a byproduct, which is essential for respiration in most living organisms.
- Climate regulation: Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to regulate global temperatures.
- Ecosystem foundation: Plants, the producers in ecosystems, form the base of the food chain, providing sustenance for herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers.
Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab Answer Key
Conclusion
The Gizmo Student Exploration Photosynthesis Lab is a valuable tool for students and enthusiasts eager to explore the fascinating world of plant life. By understanding photosynthesis, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate processes driving life on Earth. Remember to experiment, explore, and share your discoveries with others to foster a greater understanding of this essential process. Are you ready to delve into the mysteries of photosynthesis using the Gizmo lab? Let us know in the comments below!






