Imagine a world without motors – no conveyor belts in factories, no pumps circulating water, no electric vehicles speeding across the roads. It’s hard to fathom, isn’t it? Motors are the workhorses of modern industry, and at the heart of their operation lies the intricate dance of electricity – a dance orchestrated by the humble motor starter.

Image: ipendsic.blogspot.com
For those unfamiliar, a motor starter is essentially a control device that manages the flow of electricity to a motor, ensuring a safe and controlled start-up and shutdown. When dealing with powerful three-phase motors, understanding the wiring diagram of a 3-phase motor starter becomes paramount. This intricate network of wires and components is the language of power, and deciphering it unlocks the secrets to efficiently controlling and protecting these vital machines.
Unveiling the Components of a 3-Phase Motor Starter
Before diving into the wiring diagram intricacies, let’s first understand the components that make up a 3-phase motor starter. Each element plays a specific role in ensuring the smooth and safe operation of the motor:
1. The Motor: The Heart of the System
At the very core of the system, we have the electric motor itself. Three-phase motors utilize alternating current, with three phases of electricity flowing through separate windings. This configuration allows for high power output, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
2. The Contactor: The Gatekeeper of Power
The contactor acts as a switch – a gatekeeper that controls the flow of power to the motor. It consists of electromagnetic coils that, when energized, attract movable contacts, closing an electrical circuit and allowing power to reach the motor.
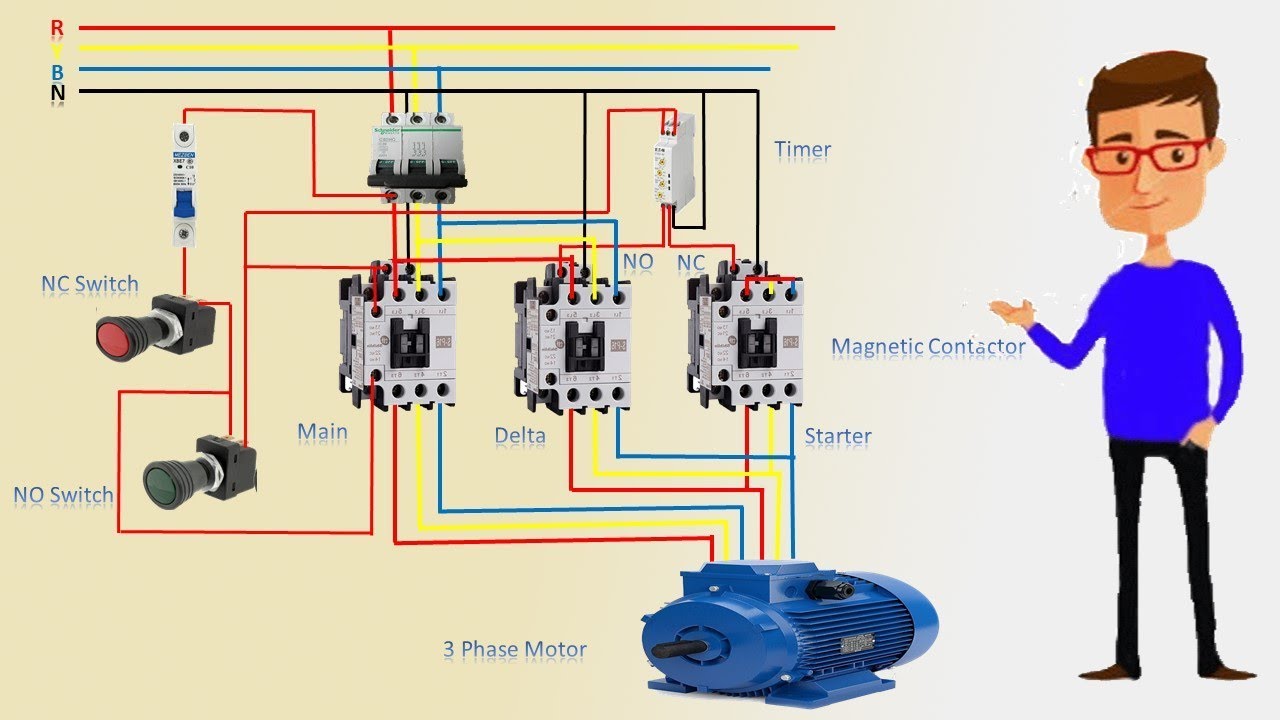
Image: manual.imagenes4k.com
3. Overload Relay: The Safety Sentinel
As the name suggests, overload relays serve as safety guardians, watching over the motor’s current consumption. When excessive current flows due to overload or motor jams, the overload relay trips, breaking the circuit and disconnecting the motor to prevent damage.
4. Fuse: The Last Line of Defense
Fuses are the ultimate safety measure, acting as sacrificial devices to protect the entire system. They are designed to melt and break the circuit in case of a short circuit or excessive current flow, preventing catastrophic damage to the motor or wiring.
5. Control Circuit: The Command Center
This circuit acts as the brain of the starter, receiving control signals from switches, sensors, or a control panel and initiating the contactor to energize or de-energize the motor. It may include components like pushbuttons, limit switches, and relay circuits.
Decoding the 3-Phase Motor Starter Wiring Diagram
Now, let’s embark on understanding the wiring diagram itself. This seemingly complex web of lines and symbols holds the key to setting up and troubleshooting the motor starter.
1. The Power Connection: Feeding the Motor
The journey begins with the power source, typically a three-phase power supply. Lines L1, L2, and L3 represent the three phases of incoming power. These lines are connected to the contactor’s terminals, feeding the motor through the contactor’s main contacts.
2. The Control Circuit: Issuing Commands
The control circuit is the brain behind the operation. It receives signals from various sources, such as pushbuttons, limit switches, or even programmable logic controllers (PLCs). These signals travel through the wiring diagram to energize the contactor coil, initiating the motor start-up.
3. The Overload Relay: Monitoring the Motor
The overload relay is wired in series with the motor. Its coils monitor motor current, and if an overload condition is detected, the relay’s contacts open, breaking the power supply to the motor and protecting it.
4. The Fuse: The Final Line of Defense
Fuses are typically mounted in the power supply circuit, acting as the ultimate safety measure. If a fault occurs in the power supply circuit, the fuse will melt and break the circuit, preventing damage to the entire system.
Benefits of Using 3-Phase Motor Starters
Why are 3-phase motor starters so integral to industrial operations? The answer lies in the multitude of benefits they deliver:
1. Enhanced Safety: Protecting the Motor and Workers
Motor starters are crucial for worker safety. They prevent direct contact with high-voltage components, and the overload and fuse protection mechanisms safeguard the motor from damage and potential hazards.
2. Controlled Startup: Ensuring Smooth Motor Operation
Sudden surges of power can damage motors. Motor starters provide gradual start-up, minimizing stress on the motor and ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
3. Easy Control and Automation: Integrating with Automation Systems
3-phase motor starters can be easily incorporated into automation systems, allowing for remote control and monitoring, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
4. Enhanced Motor Lifespan: Protecting the Investment
By preventing overload, short circuits, and other harmful conditions, motor starters effectively extend the lifespan of expensive motors, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right 3-Phase Motor Starter: Matching Needs and Applications
While understanding the concept is crucial, choosing the right starter, which requires considering specific needs and applications. You need to match the starter’s capacity and features to the motor’s requirements.
1. Size and Power Capacity: Aligning with Motor Requirements
The starter’s size and power rating must match the motor’s specifications. A starter that is too small will overload, while one that is too large will be inefficient.
2. Contactor Type: Leveraging Specific Features
Conductors come in different types, such as AC or DC, with varying voltage and current ratings. The type of contactor should correspond to the motor’s operating conditions.
3. Overload Protection: Selecting Appropriate Settings
The overload relay’s settings should correspond to the motor’s characteristics, such as its current rating and operating temperature.
4. Control Circuit Features: Tailoring to Automation Requirements
Control circuit features may include pushbuttons, limit switches, or PLC interfaces. The selection depends on the control system and the automation requirements.
Safety Precautions: Respecting the Power
Working with electrical systems, especially high-voltage equipment, demands utmost care and caution. Here are some essential safety measures to follow:
1. De-energize the System: Breaking the Circuit
Always disconnect power from the motor starter before working on it. This ensures a safe work environment and prevents potential electrocution hazards.
2. Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Preventing Accidental Energization
Implement lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization while working on the system. This ensures that no one can unknowingly switch the power back on during maintenance.
3. Use Appropriate Safety Equipment: Protecting Yourself
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves, safety glasses, and rubber-soled shoes, when working with electrical systems.
4. Train and Supervise: Ensuring Competence
Only qualified and trained personnel should work on 3-phase motor starters. Supervision and proper safety protocols are crucial.
3 Phase Motor Starter Wiring Diagram
Conclusion
The world of 3-phase motor starters may seem intimidating at first glance, but with an understanding of its components, wiring, and essential principles, we can harness its power safely and effectively. This intricate dance of electricity, when properly understood and implemented, empowers industries to operate smoothly, efficiently, and safely.
As we have seen, comprehending the 3-phase motor starter wiring diagram is not merely about technical knowledge; it’s about unlocking the potential of industrial power, ensuring efficiency, safety, and the seamless operation of critical machinery. So, let’s embrace this knowledge, respect the power we wield, and continue to innovate, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the world of industrial automation.






