Have you ever wondered how to count to one hundred in Hindi? It’s a fascinating journey that takes you through a world of vibrant sounds, intriguing grammar, and a rich cultural heritage. Learning to count in Hindi is not just about memorizing numbers; it’s a gateway to understanding the language, culture, and history of millions of people around the globe. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of Hindi numeration, delving into its history, exploring its unique structure, and revealing how numbers weave a tapestry of everyday life in the Hindi-speaking world.
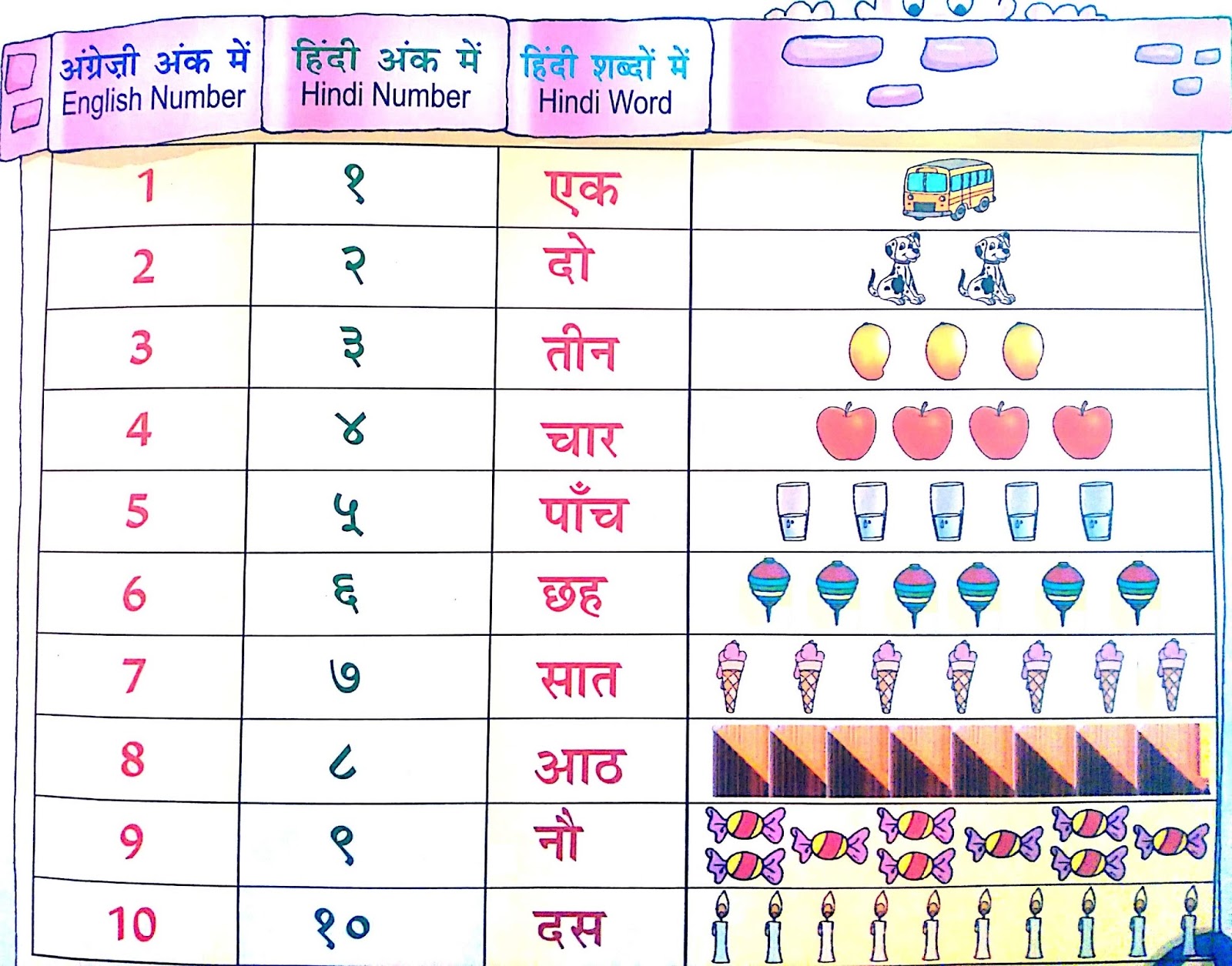
Image: mavink.com
From the simple “ek” (one) to the grand “sau” (one hundred), the Hindi counting system is a captivating journey, both simple and profound. Every number holds a story, a connection to the past, and a link to the present. Imagine yourself stepping into an bustling Indian marketplace, where vendors call out prices with the melodious cadence of Hindi numerals. This article becomes your personal guide, unlocking the secrets of this age-old numeration system and inviting you to join the vibrant world of Hindi counting.
A Glimpse into the Historical Roots of Hindi Counting
The numbers we use today in Hindi have their origins in a fascinating historical journey. They arrived in India through the medium of Sanskrit, a language with a rich history spanning millennia. The ancient Indian civilization developed a sophisticated system of numerals, and these numerals, often referred to as Brahmi numerals, laid the foundation for the number system used in Hindi. These ancient numerals, although visually distinct from the modern ones, were the predecessors of the numerals we use today in Hindi.
The evolution of Hindi numbers was a process of adaptation and evolution, shaped by influences from various cultures and empires. The arrival of the Gupta era (320-550 CE) marked a significant turning point, as this era witnessed a refined and simplified form of Brahmi numerals that would later influence the development of the Arabic numeral system. The Arabic numeral system, borrowed from the Gupta numerals, eventually spread throughout the world.
Numbers from “Ek” to “Das”: The Foundation of Hindi Counting
Let’s embark on our journey from the very beginning, learning the first ten numbers in Hindi:
The First Ten Numbers:
- Ek (१) – One
- Do (२) – Two
- Teen (३) – Three
- Chaar (४) – Four
- Panch (५) – Five
- Chhe (६) – Six
- Saat (७) – Seven
- Aath (८) – Eight
- Nau (९) – Nine
- Das (१०) – Ten
Notice that the pronunciations are relatively straightforward. Most of the words have only one syllable, making them easy to remember.
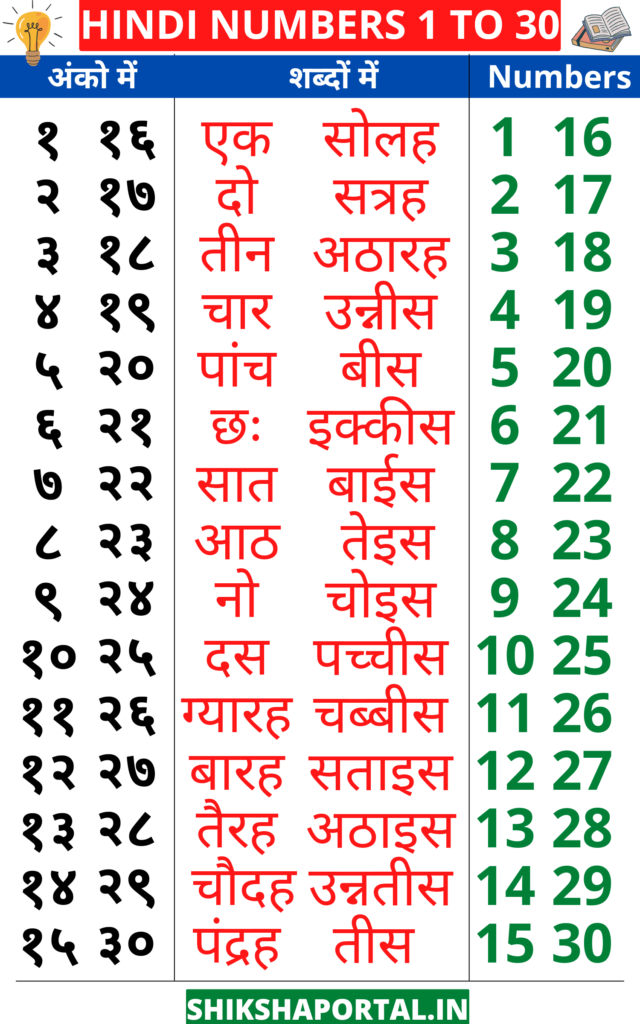
Image: shikshaportal.in
Building the Bridge to Hundred: Numbers 11-19
Now let’s expand our horizons by learning numbers from eleven to nineteen. This range reveals a unique characteristic of the Hindi counting system.
The Numbers 11-19:
- Gyaraah (११) – Eleven
- Baarah (१२) – Twelve
- Terah (१३) – Thirteen
- Chaudah (१४) – Fourteen
- Pandraah (१५) – Fifteen
- Soleh (१६) – Sixteen
- Satrah (१७) – Seventeen
- Aatharah (१८) – Eighteen
- Unnis (१९) – Nineteen
Notice that the numbers from eleven to nineteen are constructed by combining the numbers one through nine with the word “das” (ten). For example, “gyaraah” (eleven) is formed by joining “ek” (one) and “das” (ten).
Unlocking the Pattern: Numbers 20-99
Let’s now unveil the pattern for numbers beyond ten. In Hindi, we express the numbers from twenty to ninety by combining the numbers two through nine with the word “bees” (twenty), “tees” (thirty), “chalis” (forty) and so on. Let’s explore these unique combinations:
Number 20-99:
- Bees (२०) – Twenty
- Tees (३०) – Thirty
- Chalis (४०) – Forty
- Pachas (५०) – Fifty
- Saath (६०) – Sixty
- Sattar (७०) – Seventy
- Aassi (८०) – Eighty
- Nawwe (९०) – Ninety
And to form numbers like twenty-one, twenty-two, and so on, we add the numbers one through nine to these base numbers. For example, “ekis” (२१) is twenty-one, “baais” (२२) is twenty-two, and so on.
Reaching the Pinnacle: “Sau” – One Hundred
Finally, we reach the pinnacle, “sau” (१००) – one hundred. This number signifies a milestone, a completion, and a new beginning.
Beyond “Sau”:
Beyond one hundred, the Hindi counting system continues to follow this pattern. “Ek sau ek” (१०१) translates to one hundred one, “ek sau do” (१०२) is one hundred two, and so on. We simply add the numbers one through ninety-nine to one hundred. For larger numbers, the system expands with the introduction of “hazaar”(१०००) – one thousand, “lakh” (१००,०००)- one hundred thousand, and “crore” (१०,०००,०००)- ten million.
Beyond Counting: The Practical Applications of Hindi Numbers
Learning the Hindi numbers can open up a world of possibilities. It can enhance your travel experiences, improve your communication with Hindi speakers, and deepen your understanding of Hindi culture.
- Travel: Knowing Hindi numbers will make your trips to India more enriching. You can interact with locals, ask for directions, and even haggle at markets, effectively.
- Communication: Whether you’re learning Hindi as a language or simply want to connect with Hindi speakers, numbers are the building blocks that form the foundation for everyday conversations.
- Cultural Understanding: Hindi numbers are not just numerals; they are embedded in many aspects of Indian culture, from the rhythms of traditional music to the intricate patterns of art and architecture. Understanding the way numbers are used in Hindi literature can reveal deeper insights into the culture.
Counting In Hindi 1 To 100
https://youtube.com/watch?v=1qhWmLqgoVg
A Final Thought: Embracing the Journey of Hindi Counting
Counting in Hindi is more than just memorizing numbers; it’s about immersing yourself in a vibrant culture, connecting with a rich heritage, and expanding your understanding of the world. Every time you say “ek” (one), “do” (two), or “sau” (one hundred), you’re taking a step closer to appreciating the beauty and depth of the Hindi language and culture. So, why not embark on this journey, one number at a time, and let the magic of Hindi numbers unfold?






