Imagine waking up in the middle of the night, desperate to relieve yourself, only to find your body unable to cooperate. Or picture the struggle of managing incontinence, the constant worry of an unexpected accident. These experiences, though often unspoken, are realities for countless individuals facing impaired urinary elimination. This complex issue goes beyond simple discomfort; it significantly impacts self-esteem, social participation, and overall well-being.

Image: www.vrogue.co
This article delves into the world of impaired urinary elimination, providing you with essential knowledge and empowering you with practical strategies for self-care and support for loved ones. We’ll explore the causes, challenges, and the key roles of nursing care in managing this condition. Together, we’ll navigate the intricacies of urinary elimination, unraveling the complexities to equip you with the tools to live a more comfortable and fulfilling life.
Understanding Impaired Urinary Elimination: A Multifaceted Challenge
Impaired urinary elimination encompasses a range of conditions that interfere with the body’s ability to control urination. These conditions can be temporary, as in the case of urinary tract infections (UTIs), or chronic, often stemming from underlying medical conditions.
Common Causes of Impaired Urinary Elimination
A diverse set of factors can contribute to urinary elimination issues:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): These infections, commonly caused by bacteria, trigger inflammation in the bladder and urethra, leading to frequent and painful urination.
- Bladder Control Issues: Age-related changes, neurological conditions, or damage to the nerves controlling the bladder can lead to incontinence, making it difficult to hold urine.
- Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, BPH): The prostate gland, located at the base of the bladder, can enlarge with age, putting pressure on the urethra and hindering urine flow.
- Neurological Conditions: Conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson’s disease, and stroke can affect the nerves controlling bladder function, resulting in impaired elimination.
- Medications: Certain medications, like diuretics, can increase urine production and lead to more frequent urination.
- Structural Anomalies: In rare cases, birth defects or injuries can cause anatomical abnormalities that affect bladder function.
Navigating the Challenges: The Impact of Impaired Urinary Elimination
Living with impaired urinary elimination often poses significant challenges:
- Physical Discomfort: Frequent urination, urgency, pain, and accidents can significantly impact quality of life and limit activity levels.
- Social Isolation: Embarrassment and fear of social situations can lead to withdrawing from social interactions and activities.
- Psychological Distress: The emotional impact can be significant, contributing to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
- Impact on Relationships: Managing the condition can strain relationships with loved ones and partners, leading to decreased intimacy and emotional distance.
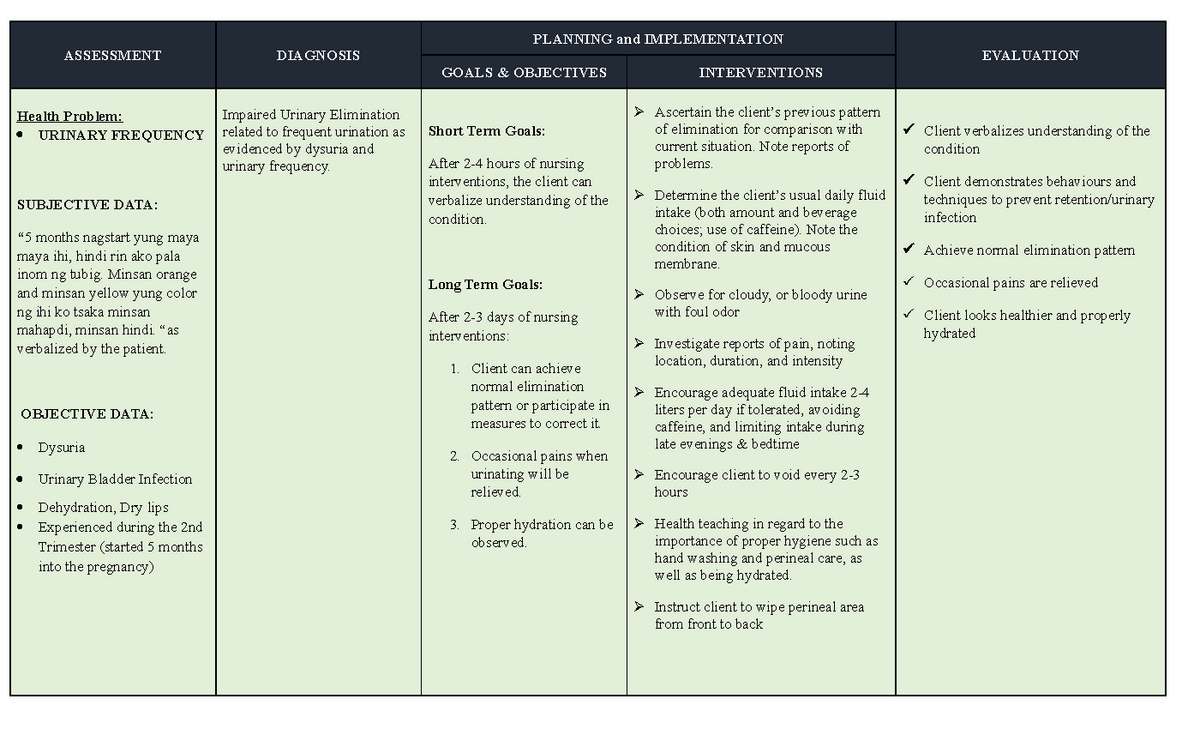
Image: www.vrogue.co
The Role of Nursing Care: A Collaborative Approach
Nursing care plays a crucial role in managing impaired urinary elimination, ensuring overall well-being and quality of life.
Assessment and Diagnosis
Nurses are instrumental in assessing individuals with urinary issues. This involves gathering a thorough history, including medication use, past medical conditions, and symptoms. Physical examinations, including palpation of the bladder, are undertaken to identify any abnormalities.
Establishing a Nursing Care Plan
A comprehensive nursing care plan is developed in collaboration with the patient, their family, and other healthcare professionals. This plan is tailored to address individual needs:
- Educating the patient about their condition: Providing clear and accurate information about the cause, management, and potential complications can empower individuals to take an active role in their care.
- Developing bladder training programs: Through regular toileting schedules and techniques like timed voiding, individuals can train their bladders to hold urine for longer periods.
- Implementing strategies for urinary incontinence: Depending on the type of incontinence, interventions like absorbent pads, pelvic floor exercises, or medication can be prescribed.
- Promoting hydration and dietary modifications: Adequate fluid intake is essential for healthy urination, while limiting caffeine and alcohol can help reduce bladder irritation.
- Addressing psychosocial concerns: Nurses provide emotional support, help individuals cope with the emotional challenges, and refer them to mental health professionals if needed.
Providing Ongoing Support
Nurses continue to provide ongoing support and education, enabling individuals to manage their condition effectively:
- Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions: Regular assessments are conducted to gauge the patient’s progress and adjust the care plan accordingly.
- Identifying potential complications and taking immediate action: Early identification of complications, such as UTIs or skin breakdown, can help prevent further health issues.
- Building confidence and independence:` Nurses empower individuals to manage their condition by providing them with the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions about their care.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips: Empowering Your Care
Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned urologist, emphasizes the importance of proactive management: “Early intervention is key to preventing complications and improving long-term outcomes.”
Here are actionable tips you can implement today:
- Keep a bladder diary: Maintain a record of your urination habits, including the frequency, urgency, and any associated pain. This diary provides valuable insights for diagnosis and treatment.
- Engage in pelvic floor exercises: Also known as Kegel exercises, these strengthen the muscles that control urination, aiding in bladder control.
- Seek support from a trusted healthcare professional: Don’t hesitate to reach out to a nurse or doctor for guidance and treatment options.
Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Urinary Elimination
Conclusion: Embracing Hope and Empowering Yourself
Impaired urinary elimination can be a challenging journey, but with the right knowledge and support, you can navigate it with greater confidence and control. Remember, you are not alone. Nurses are your trusted partners in managing this condition, providing personalized care and empowering you to live a fulfilling life. Don’t hesitate to seek professional support and embark on this journey towards a healthier and more comfortable future.






