Imagine a world where your body can’t properly use the fuel it needs to function. This is the reality for millions of people living with diabetes, a chronic condition that affects how their bodies regulate blood sugar levels. It’s a daunting prospect, but understanding the intricate dance of insulin signaling and its impact on diabetes is crucial for managing this disease effectively.
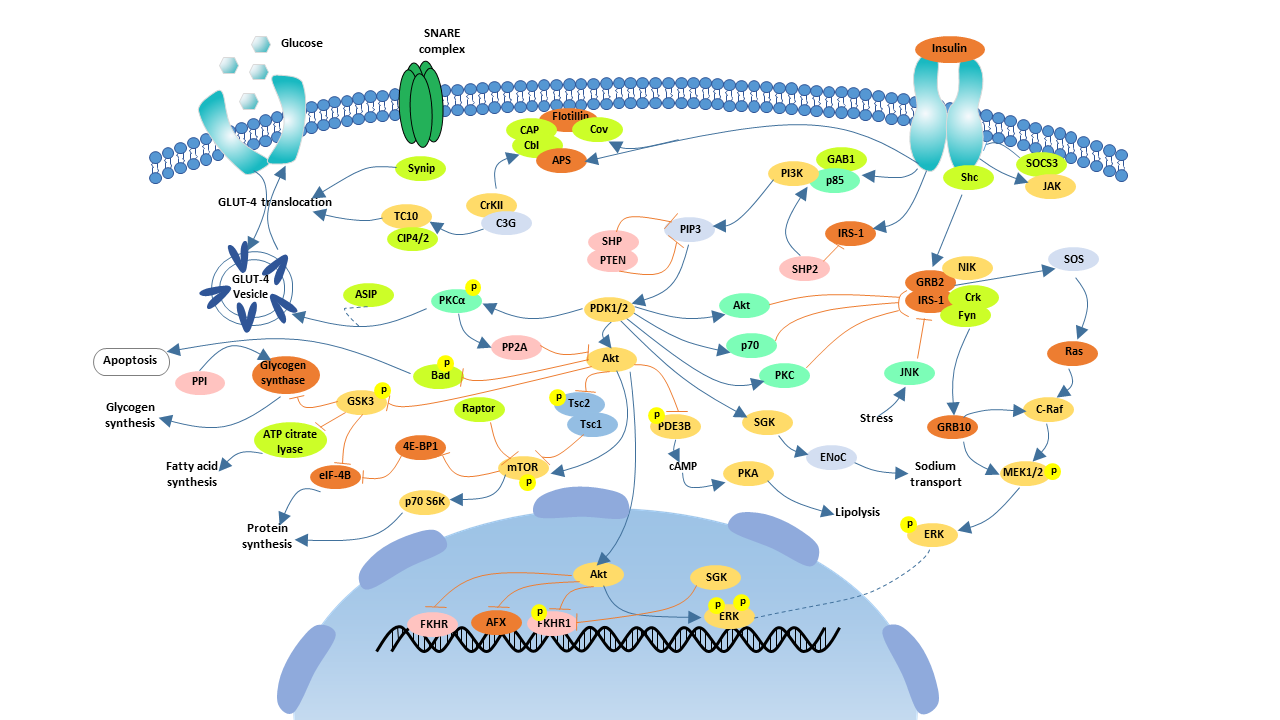
Image: mungfali.com
My own journey learning about diabetes began when my grandmother was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Witnessing her struggle to manage her blood sugar levels, I was drawn to the complexities of insulin resistance and its role in this complex metabolic disorder. It sparked a passion to understand the science behind it, which eventually led me to delve into the world of insulin signaling, a fascinating cascade of events that orchestrate glucose metabolism in our bodies.
Unveiling the Insulin Signaling Pathway: A Complex Symphony of Regulation
At the heart of diabetes lies a malfunctioning insulin signaling pathway. This intricate network of cellular signals acts like a conductor, leading the body’s orchestra of metabolism. When insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, binds to its receptor on cells, it sets off a chain reaction of events. This chain reaction activates a series of enzymes and proteins, ultimately allowing glucose to enter cells and be utilized as energy.
However, in individuals with diabetes, this delicate dance becomes disrupted. In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to an absolute deficiency of insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the body develops resistance to insulin, meaning the cells don’t respond as effectively to the hormone, leading to a buildup of sugar in the bloodstream. Understanding the intricacies of this signaling pathway is crucial for developing effective therapies that can restore balance and improve the lives of those living with diabetes.
Deciphering the Complexity of Insulin Signaling
A Detailed Look at the Pathway
The insulin signaling pathway is a complex network of interconnected processes that involves a variety of proteins and enzymes. It begins when insulin binds to its receptor, a transmembrane protein located on the surface of cells. This binding event triggers a cascade of phosphorylation events, where phosphate groups are added to specific proteins, activating or inhibiting their function.
One of the key events in this cascade is the activation of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins. These proteins act as signal transducers, relaying the insulin signal further down the pathway. Activation of IRS proteins leads to the recruitment of other signaling molecules, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (Akt).
PI3K plays a crucial role in regulating glucose uptake, while Akt promotes cell growth and survival. The insulin-signaling pathway is a vital process for regulating blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, particularly in skeletal muscle and fat tissues. These cells utilize glucose as their primary energy source, while excess glucose is converted to glycogen for storage.
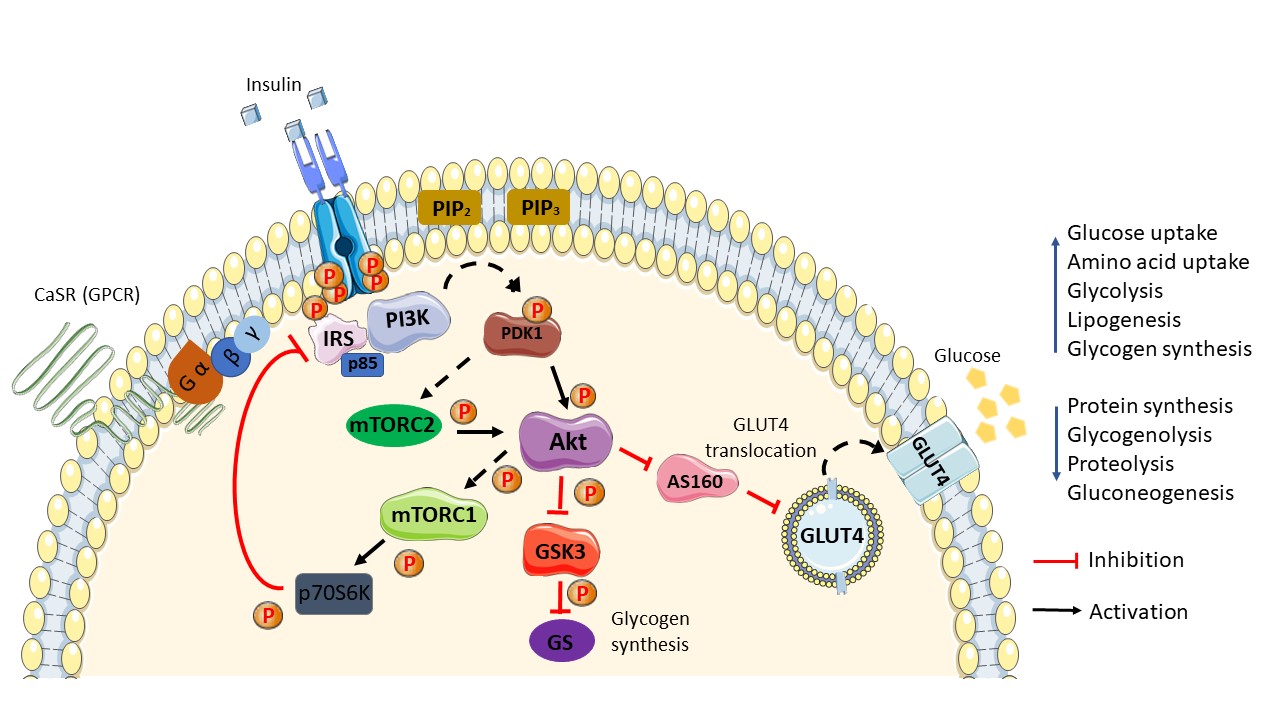
Image: encyclopedia.pub
The Importance of Insulin Sensitivity
The efficiency of insulin signaling, often referred to as insulin sensitivity, is crucial for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. When insulin sensitivity is impaired, the body requires higher levels of insulin to achieve the same effect, leading to insulin resistance. This resistance ultimately contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Several factors can contribute to insulin resistance, including genetics, lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise, and other underlying medical conditions. Research continues to explore the complex interplay of these factors and their impact on insulin signaling.
Current Trends in Diabetes Research
The field of diabetes research is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing prevalence of the disease globally. Researchers are exploring new therapies targeting various aspects of the insulin signaling pathway, including:
- Insulin Sensitizers: These drugs enhance insulin sensitivity at the cellular level, allowing the body to utilize insulin more effectively. Metformin, a widely used antidiabetic drug, acts as an insulin sensitizer.
- Incretin Mimetics: These drugs mimic the effects of incretins, gut hormones that stimulate insulin production and slow gastric emptying.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These drugs activate GLP-1 receptors, promoting insulin release and reducing glucagon secretion, ultimately lowering blood sugar levels.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: These drugs block the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, increasing its excretion in the urine and lowering blood sugar levels.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Researchers are investigating the potential of stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells, offering a potential treatment for type 1 diabetes.
These advancements offer hope for improving the management of diabetes and potentially even finding a cure.
Expert Tips for Managing Diabetes
Living with diabetes requires a proactive approach to managing blood sugar levels. Here are some tips based on current research and expert advice:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Consult with a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels Regularly: Regularly test your blood sugar levels, as instructed by your doctor, to track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Consistency is key.
- Take Medications as Prescribed: If you are prescribed insulin or other medications for diabetes, take them as directed by your healthcare provider. Don’t skip doses or adjust your medication without consulting your doctor.
- Manage Stress: Stress can contribute to blood sugar fluctuations. Practice stress-management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Remember, managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, and adopting sustainable lifestyle changes is essential for maintaining good health and preventing long-term complications.
FAQs about Diabetes and Insulin Signaling
Q: What are the main differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to an absolute insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin.
Q: Can diabetes be prevented?
While there are genetic predispositions to type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors play a significant role. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Q: What are the long-term complications of diabetes?
Uncontrolled or poorly managed diabetes can lead to various long-term complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye damage, and amputations.
Q: How can I learn more about diabetes and insulin signaling?
You can consult with your healthcare provider, explore reliable online resources such as the American Diabetes Association or the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and consider joining support groups or online communities dedicated to diabetes.
Diabetes And Insulin Signaling Case Study
Conclusion
Understanding the complex world of insulin signaling is essential for managing diabetes effectively. By unraveling the intricate mechanisms of this pathway, researchers continue to develop innovative therapies and provide hope for millions living with this chronic condition.
Are you interested in learning more about diabetes and insulin signaling? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.






