Imagine a world where you could quickly and accurately assess the severity of a stroke, empowering you to make life-saving decisions in critical moments. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is a powerful tool that helps medical professionals do just that. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of the NIHSS, providing a comprehensive guide to its certification, scoring system, and critical interpretations.
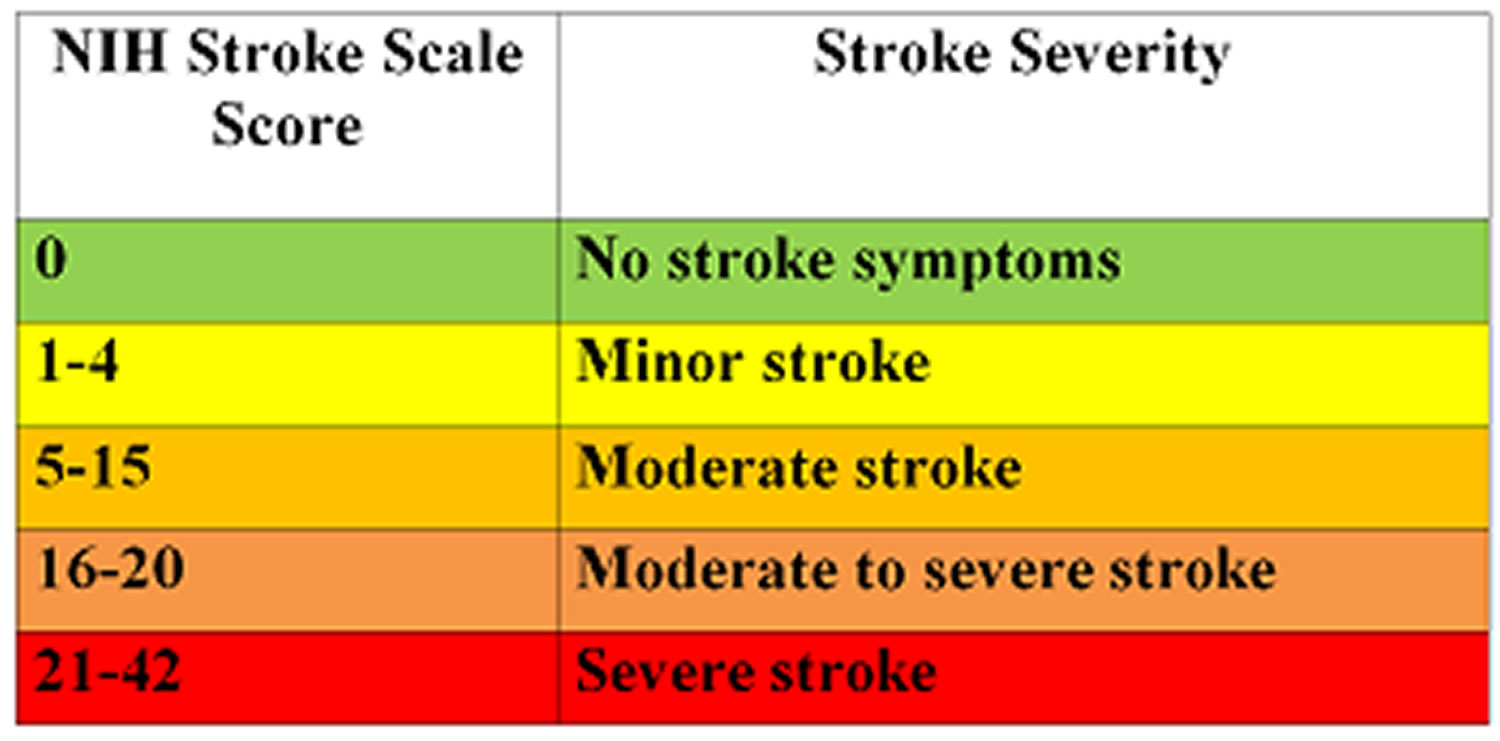
Image: healthjade.net
The NIHSS is a standardized neurological assessment tool used by doctors and nurses worldwide to evaluate stroke patients. It is a vital tool for diagnosing, classifying, and monitoring the progression of strokes, ultimately aiding in treatment and prognosis. Understanding the NIHSS is crucial not only for medical professionals but also for individuals who may encounter a stroke in their family or community. Knowing how to use the scale can provide valuable insights into the severity of the situation and potentially affect the course of treatment.
Decoding the NIHSS: An Examination of the Scoring System
The NIHSS is an 11-item scale, each assessing a different neurological function, ranging from level of consciousness to language abilities. The score ranges from 0 to 42, with higher scores indicating a more severe stroke. It is essential to understand the individual components of the scale and their corresponding scores to interpret the overall NIHSS result.
1. Level of Consciousness: (0 – 4 points)
This component assesses the patient’s alertness and responsiveness. The scale ranges from fully awake and oriented (score 0) to a state of deep coma (score 4).
2. Gaze: (0 – 3 points)
This section examines the patient’s eye movement and gaze. A score of 0 indicates normal eye movement, while a score of 3 suggests severe deviation of gaze.
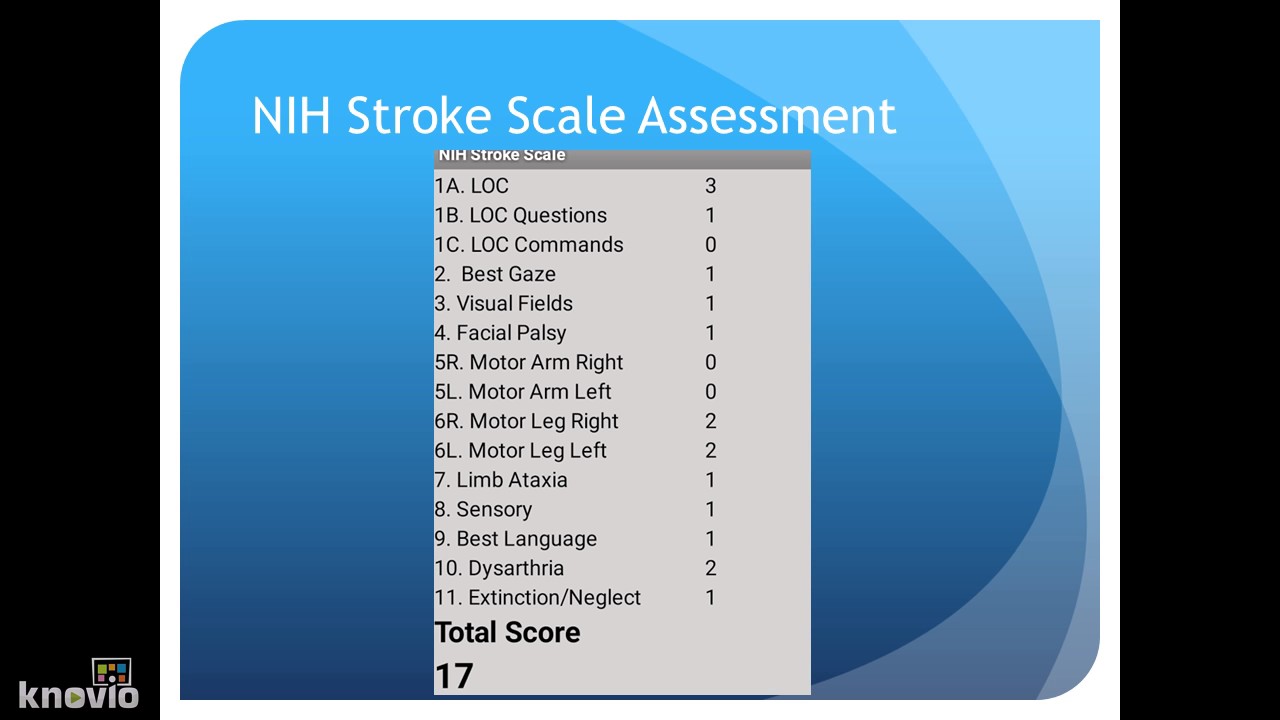
Image: www.youtube.com
3. Visual Fields: (0 – 2 points)
This component tests the patient’s ability to perceive visual stimuli. A score of 0 indicates normal vision, while a score of 2 indicates complete blindness in one eye.
4. Facial Movement: (0 – 2 points)
This section assesses facial paralysis, focusing on symmetry and movement. A score of 0 indicates a normal smile, while a score of 2 indicates complete paralysis of one side of the face.
5. Motor Function: (0 – 4 points)
This component evaluates the patient’s strength and coordination in the upper and lower extremities.
6. Limb Ataxia: (0 – 2 points)
This section tests for limb incoordination, assessing balance and stability.
7. Sensory: (0 – 2 points)
This component evaluates the patient’s sensory perception in the upper and lower extremities.
8. Language: (0 – 3 points)
This section assesses the patient’s ability to understand and express language.
9. Dysarthria: (0 – 2 points)
This component evaluates the patient’s ability to speak clearly and articulately.
10. Extinction and Inattention: (0 – 2 points)
This section examines the patient’s ability to perceive sensory stimuli simultaneously on both sides of the body.
11. Neglect: (0 – 3 points)
This final component assesses the patient’s awareness of their surroundings and their ability to attend to stimuli in both sides of their environment.
Navigating the NIHSS: A Practical Guide to Interpretation
The NIHSS score provides valuable information about the severity and location of the stroke, influencing treatment decisions and predicting long-term outcomes.
Mild Stroke (0-4):
A score of 0-4 suggests a mild stroke, with minimal neurological deficits. These patients may experience some mild weakness or numbness but usually retain most of their functional abilities.
Moderate Stroke (5-15):
A score of 5-15 indicates a moderate stroke, with more substantial neurological deficits. These patients may experience significant weakness, speech impairments, or cognitive difficulties.
Severe Stroke (16-42):
A score of 16-42 suggests a severe stroke, with severe neurological impairments. These patients may experience complete paralysis, loss of consciousness, or critical organ dysfunction.
Gaining Expertise: Embark on NIHSS Certification
The NIHSS is a powerful tool that requires specialized training and certification to use effectively. Certification programs are offered by various organizations, such as the American Heart Association (AHA) and the National Stroke Association (NSA). These programs typically involve classroom instruction, hands-on practice, and a written exam.
Benefits of NIHSS Certification:
- Enhanced knowledge, skills, and confidence in utilizing the NIHSS effectively.
- Improved ability to assess stroke severity, plan treatment, and predict long-term outcomes.
- Increased professionalism and credibility among peers and colleagues.
- Access to a network of certified professionals and resources.
Challenges and Limitations of the NIHSS
While the NIHSS is a valuable tool, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. The scale is primarily designed to assess neurological function in patients with ischemic stroke, but it may not be as effective in other stroke types, such as hemorrhagic strokes, or in patients with pre-existing neurological conditions.
Factors to Consider:
- Patient variability: Stroke severity can vary significantly between patients, even with similar NIHSS scores.
- Cognitive limitations: The NIHSS may be difficult to administer in patients with significant cognitive impairments.
- Cultural differences: Subtle cultural differences in language and nonverbal communication may affect the interpretation of the scale.
Beyond the Scoring: The Importance of Comprehensive Assessment
The NIHSS is not a standalone assessment tool but rather a valuable component of a comprehensive neurological evaluation. It is crucial to consider the patient’s medical history, imaging studies, and other diagnostic tests to obtain a complete picture of their condition and guide treatment decisions.
Nih Stroke Scale Certification A Answers
Conclusion: Navigating the Path to Stroke Expertise
The NIHSS is an indispensable tool for medical professionals, providing a standardized and reliable method to assess stroke severity and manage patient care. By understanding the intricacies of the scale and its interpretation, healthcare teams can make informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and advance the field of stroke management. If you are interested in becoming a certified NIHSS user or want to learn more about stroke management, consider enrolling in a reputable certification program or seeking guidance from a stroke specialist. Remember, continuous education and collaboration play a vital role in improving stroke care and ultimately saving lives.






