Have you ever been stuck scratching your head, trying to figure out why a circuit isn’t working? You’ve checked the fuses, everything seems connected, but there’s no power. It’s like a phantom electrical gremlin is lurking in the wires, sabotaging your efforts. Enter the power probe, your trusty sidekick for electrical troubleshooting, and its invaluable companion – the fuse voltage drop charts.
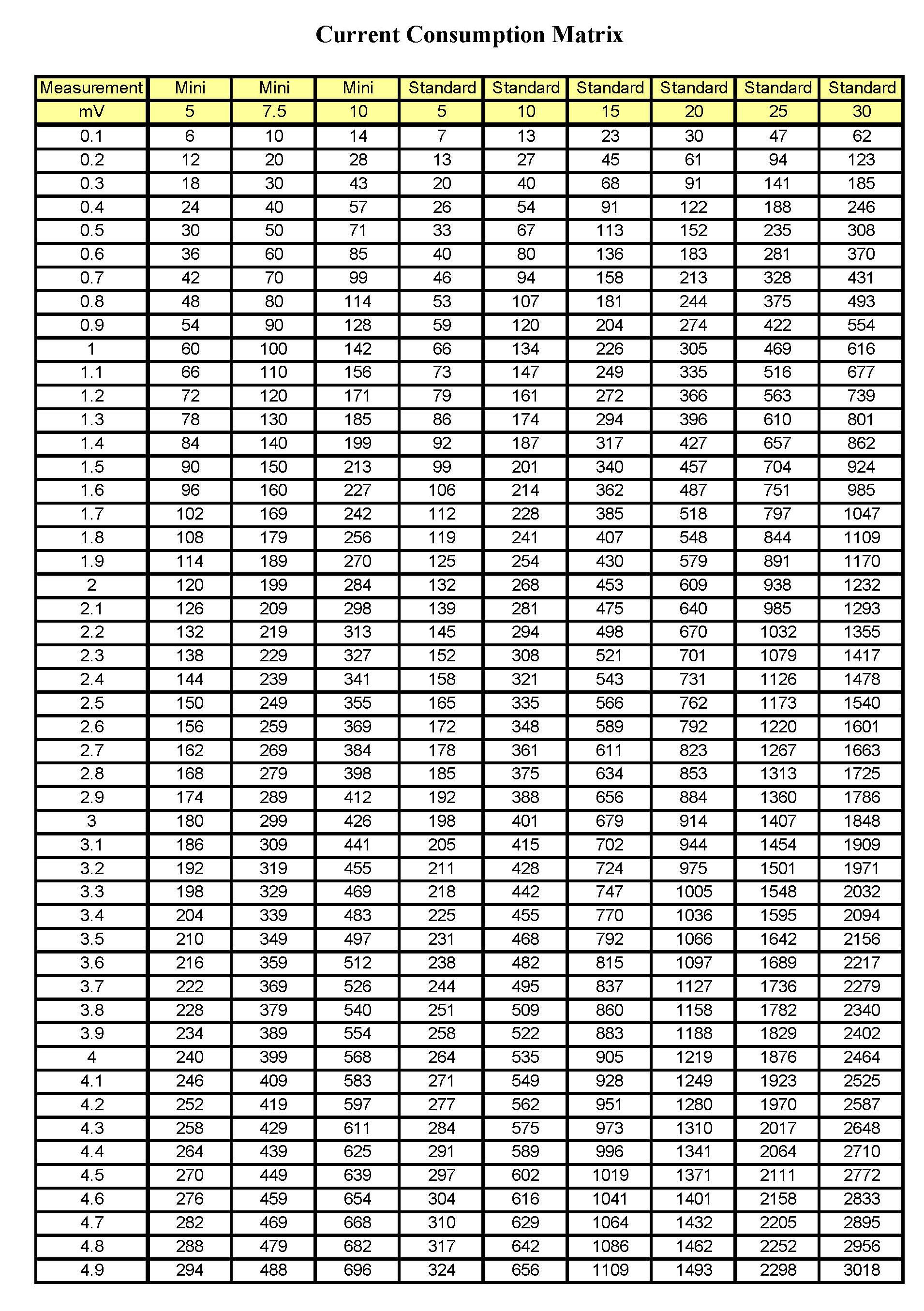
Image: katherinenorton.z21.web.core.windows.net
These charts are essential tools for pinpointing electrical issues, especially when dealing with complex wiring systems. They provide a blueprint for understanding how voltage behaves across various circuits, making it easier to diagnose problems like blown fuses, faulty wiring, or even faulty components. This article aims to guide you through the world of power probe fuse voltage drop charts, demystifying their functionality and revealing how they can become your ultimate troubleshooting weapon.
Understanding the Basics
What is a Power Probe?
A power probe is a handheld device used to test electrical circuits, typically found in automotive and electronics repair settings. It’s designed to detect voltage, continuity, and ground, providing vital insights into the health of your electrical system.
What are Fuse Voltage Drop Charts?
Fuse voltage drop charts are visual representations of how voltage changes across different points in a circuit, including fuses. They depict expected voltage readings for each fuse, providing a baseline comparison for troubleshooting purposes. If the voltage drop across a fuse is significantly higher than expected, it’s a clear indication of a problem.
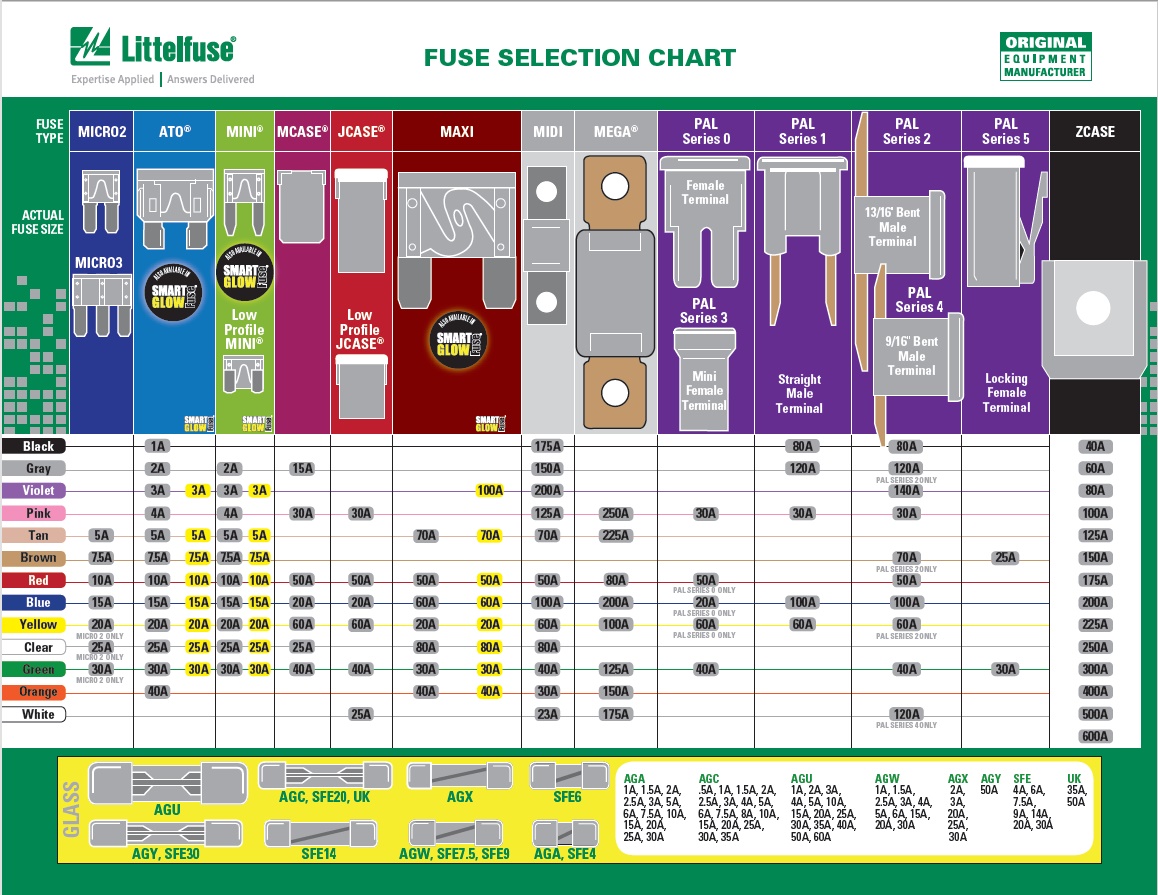
Image: classlibraryfruehauf.z19.web.core.windows.net
How Fuse Voltage Drop Charts Work
Analyzing Voltage Drop
Voltage drop occurs naturally as electricity flows through a circuit. The resistance of the wires and components creates a slight decrease in voltage along the path. Fuse voltage drop charts take this inherent drop into account, allowing you to identify unusually high drops that might be caused by faulty components, excessive resistance, or even a blown fuse itself.
Using the Charts
To use a fuse voltage drop chart, you’ll need a power probe, a voltmeter, and a copy of the specific chart for your vehicle or device. The chart will typically show the fuse location, the fuse amperage, and the expected voltage drop across each fuse terminal. By testing the voltage on each side of the fuse and comparing it to the chart’s values, you can pinpoint the source of the problem.
Common Fuse-Related Problems
Fuse voltage drop charts are particularly useful for identifying these common problems:
- Blown Fuses: A blown fuse will show a complete lack of voltage on the output side of the fuse, while the input side will have the full battery voltage.
- Faulty Wiring: A loose connection, a short circuit, or corrosion in the wiring can lead to a significant voltage drop across the fuse.
- Faulty Component: A faulty component such as a light bulb, motor, or electrical switch can overload the circuit, causing a large voltage drop across the fuse.
Power Probe Fuse Voltage Drop Charts: Your Troubleshooting Toolbox
Different Types of Charts
You can find fuse voltage drop charts for various vehicles and systems, such as automotive, HVAC, electrical panels, and even complex electronic equipment. It’s important to use the correct chart for your specific application.
DIY Charts and Online Resources
While specialized charts are available, you can often create your own using a voltmeter, power probe, and basic electrical knowledge. Several online resources also provide free fuse voltage drop charts for common vehicles and systems.
For instance, you can find detailed charts for specific vehicle models, such as the 2005 Ford Explorer, on sites like AllDatadiy. These websites often include information on specific fuse positions, ratings, and even troubleshooting tips for each circuit.
Using a Power Probe with Fuse Voltage Drop Charts: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Identify the Circuit
Determine the circuit you’re troubleshooting. Use the fuse voltage drop chart to identify the corresponding fuse, its location, and the expected voltage drop across it.
2. Connect the Power Probe
Connect the power probe to the positive terminal of the battery.
- For testing the input side of the fuse, probe the fuse terminal connected to the battery side of the circuit.
- For testing the output side of the fuse, probe the fuse terminal connected to the circuit side.
3. Observe the Voltage Reading
Read the voltage displayed on the power probe. Compare this reading to the expected voltage drop listed on your fuse voltage drop chart. A significant discrepancy might signal a problem.
4. Record the Readings
Record the voltage readings for both the input and output sides of the fuse. This will help you document the voltage drop and identify potential issues.
5. Troubleshooting and Repair
If the voltage drop readings suggest a problem, diagnose and repair the faulty component or wiring based on your findings. The chart can also provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
Safety First: Precautions When Using a Power Probe
Using a power probe is generally safe, but it’s essential to take necessary precautions:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical circuits.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks or debris.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Never use a power probe on live circuits.
</ul>Beyond Automotive: Applications of Fuse Voltage Drop Charts
While commonly used in automotive troubleshooting, fuse voltage drop charts are not limited to vehicles. They can be applied to numerous electrical systems:
- HVAC Systems: Troubleshooting issues related to heating, cooling, and ventilation systems.
- Household Electrical Panels: Identifying issues with wiring, circuit breakers, and appliances.
- Industrial Equipment: Diagnosing electrical problems in heavy machinery and industrial processes.
- Electronic Devices: Troubleshooting power supply circuits and other components in electronic devices.
Power Probe Fuse Voltage Drop Charts
Conclusion
Understanding fuse voltage drop charts and mastering the power probe is a valuable skill for anyone working with electrical systems. By grasping the concepts of voltage drop, using the charts effectively, and taking necessary safety precautions, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle electrical challenges, saving time, frustration, and possibly even money in the long run. As you gain experience, you’ll find these tools become an integral part of your troubleshooting arsenal, allowing you to confidently diagnose and repair complex electrical problems with precision. So, next time you encounter a baffling electrical puzzle, grab your power probe and your fuse voltage drop charts and get ready to crack the code!






